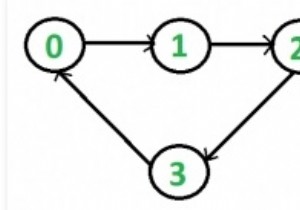
डीएजी (डायरेक्टेड एसाइक्लिक ग्राफ) का टोपोलॉजिकल सॉर्टिंग वर्टिस का एक रेखीय क्रम है जैसे कि प्रत्येक निर्देशित किनारे यूवी के लिए, जहां वर्टेक्स यू क्रम में वी से पहले आता है। यदि ग्राफ़ डीएजी नहीं है, तो ग्राफ़ के लिए टोपोलॉजिकल सॉर्टिंग संभव नहीं है।
कार्य और छद्म कोड
Begin function topologicalSort(): a) Mark the current node as visited. b) Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex. c) Push current vertex to stack which stores result. End Begin function topoSort() which uses recursive topological sort() function: a) Mark all the vertices which are not visited. b) Call the function topologicalSort(). c) Print the content. End
उदाहरण
#include<iostream>
#include <list>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
class G {
int n;
list<int> *adj;
//declaration of functions
void topologicalSort(int v, bool visited[], stack<int> &Stack);
public:
G(int n); //constructor
void addEd(int v, int w);
void topoSort();
};
G::G(int n) {
this->n = n;
adj = new list<int> [n];
}
void G::addEd(int v, int w) // add the edges to the graph. {
adj[v].push_back(w); //add w to v’s list
}
void G::topologicalSort(int v, bool visited[], stack<int> &Stack) {
visited[v] = true; //mark current node as visited
list<int>::iterator i;
//Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex.
for (i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)
if (!visited[*i])
topologicalSort(*i, visited, Stack);
Stack.push(v);
}
void G::topoSort() {
stack<int> Stack;
bool *visited = new bool[n];
//Mark all the vertices which are not visited.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
visited[i] = false;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (visited[i] == false)
//Call the function topologicalSort().
topologicalSort(i, visited, Stack);
while (Stack.empty() == false) {
cout << Stack.top() << " "; //print the element
Stack.pop();
}
}
int main() {
G g(6);
g.addEd(4, 2);
g.addEd(5, 1);
g.addEd(4, 0);
g.addEd(3, 1);
g.addEd(1, 3);
g.addEd(3, 2);
cout << " Topological Sort of the given graph \n";
g.topoSort();
return 0;
} आउटपुट
Topological Sort of the given graph 5 4 1 3 2 0