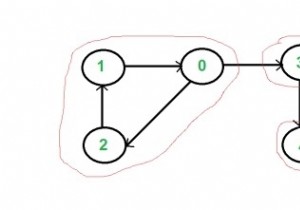
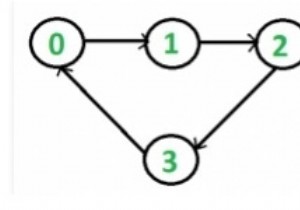
एक ग्राफ एक पेड़ है यदि इसमें कोई चक्र नहीं है। यह एक सी ++ प्रोग्राम है जो यह जांचने के लिए है कि एक अप्रत्यक्ष ग्राफ पेड़ है या नहीं।
एल्गोरिदम
Begin function cyclicUtil() : A) Mark the current node as visited. B) Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex. C) If an adjacent is not visited, then recur for that adjacent. D) If an adjacent is visited and not parent of current vertex, then there is a cycle. End Begin function cyclic(): A) Mark all the vertices as not visited and not part of recursion stack. B) Call the recursive function cyclicUtil() to detect cycle in differentDFS trees. End
उदाहरण
#include<iostream>
#include <list>
#include <limits.h>
using namespace std;
class G {
int n;
list<int> *adj;
bool CyclicUtil(int v, bool visited[], int par);
public:
G(int n); //constructor
void addEd(int v, int w);
bool cyclic();
};
G::G(int n) {
this->n = n;
adj = new list<int> [n];
}
void G::addEd(int v, int u)//to add edges in the graph {
adj[v].push_back(u); //add u to v’s list
adj[u].push_back(v);//add v to u’s list
}
//recusive function uses visited[] to detect cycle in subgraph reachable from vertex v:
bool G::CyclicUtil(int v, bool visited[], int par) {
visited[v] = true; // Mark the current node as visited
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
list<int>::iterator i;
for (i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i) {
if (!visited[*i]) //If an adjacent is not visited, then recur for that adjacent {
if (CyclicUtil(*i, visited, v))
return true;
}
// If an adjacent is visited and not parent of current vertex, then there is a cycle.
else if (*i != par)
return true;
}
return false;
}
// to check if the graph is tree or not.
bool G ::cyclic() {
bool *visited = new bool[n]; // Mark all the vertices as not visited and not part of recursion stack
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Call the recursive function CyclicUtil() to detect cycle in different DFS trees
for (int u = 0; u < n; u++)
if (!visited[u])
if (CyclicUtil(u, visited, -1))
return true;
return false;
}
int main() {
G g1(4);
g1.addEd(0, 1);
g1.addEd(1, 2);
g1.cyclic() ? cout << "Undirected Graph isn't a tree\n" : cout
<< "Undirected Graph is a tree\n";
return 0;
} आउटपुट
Undirected Graph is a tree