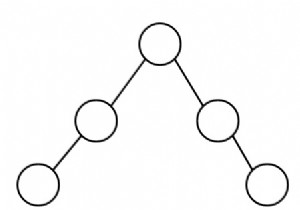
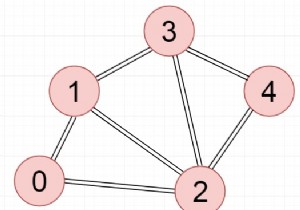
एक द्विदलीय ग्राफ एक ग्राफ है जिसमें यदि केवल दो रंगों का उपयोग करके ग्राफ को रंगना संभव है; एक समुच्चय के शीर्षों को एक ही रंग से रंगा जाता है। यह एक C++ प्रोग्राम है जो यह जांचने के लिए है कि ग्राफ़ द्विदलीय है या नहीं DFS का उपयोग कर रहा है।
एल्गोरिदम
Begin An array color[] is used to stores 0 or 1 for every node which denotes opposite colors. Call function DFS from any node. If the node w has not been visited previously, then assign ! color[v] to color[w] and call DFS again to visit nodes connected to w. If at any instance, color[u] is equal to !color[v], then the node is bipartite. Modify the DFS function End
उदाहरण
#include<iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void addEd(vector<int> adj[], int w, int v) //adding edge to the graph
{
adj[w].push_back(v); //add v to w’s list
adj[v].push_back(w); //add w to v’s list
}
bool Bipartite(vector<int> adj[], int v,
vector<bool>& visited, vector<int>& color)
{
for (int w : adj[v]) {
// if vertex w is not explored before
if (visited[w] == false) {
// mark present vertex as visited
visited[w] = true;
color[w] = !color[v]; //mark color opposite to its parents
if (!Bipartite(adj, w, visited, color))
return false;
}
// if two adjacent are colored with same color then the graph is not bipartite
else if (color[w] == color[v])
return false;
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
int M = 6;
vector<int> adj[M + 1];
// to keep a check on whether a node is discovered or not
vector<bool> visited(M + 1);
vector<int> color(M + 1); //to color the vertices of
the graph with 2 color
addEd(adj, 3, 2);
addEd(adj, 1, 4 );
addEd(adj, 2, 1);
addEd(adj, 5, 3);
addEd(adj, 6, 2);
addEd(adj, 3, 1);
visited[1] = true;
color[1] = 0;
if (Bipartite(adj, 1, visited, color)) {
cout << "Graph is Bipartite";
} else {
cout << "Graph is not Bipartite";
}
return 0;
} आउटपुट
Graph is not Bipartite