यूलर पथ एक पथ है; जिससे हम हर नोड पर ठीक एक बार विजिट कर सकते हैं। हम एक ही किनारों को कई बार इस्तेमाल कर सकते हैं। यूलर सर्किट एक विशेष प्रकार का यूलर पथ है। जब यूलर पथ का प्रारंभिक शीर्ष भी उस पथ के अंतिम शीर्ष से जुड़ा होता है।
यूलर पथ का पता लगाने के लिए, हमें इन शर्तों का पालन करना होगा
- ग्राफ़ कनेक्ट होना चाहिए।
- अब जब एक अप्रत्यक्ष ग्राफ के किसी भी कोने में विषम डिग्री नहीं होती है, तो यह एक यूलर सर्किट होता है, जो एक यूलर पथ भी होता है।
- जब ठीक दो शीर्षों में विषम डिग्री होती है, तो यह एक यूलर पथ होता है।
इनपुट
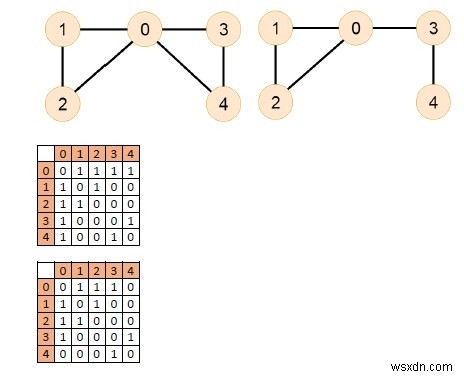
आउटपुट
दोनों ग्राफ़ में यूलर पथ हैं।
एल्गोरिदम
ट्रैवर्स(यू, विजिट किया गया)
इनपुट:प्रारंभ नोड u और विज़िट किए गए नोड को चिह्नित करने के लिए कि किस नोड का दौरा किया गया है।
आउटपुट :सभी जुड़े हुए शीर्षों को पार करें।
Begin mark u as visited for all vertex v, if it is adjacent with u, do if v is not visited, then traverse(v, visited) done End
कनेक्टेड है(ग्राफ)
इनपुट :ग्राफ़।
आउटपुट :यदि ग्राफ़ कनेक्ट है तो सही है।
Begin define visited array for all vertices u in the graph, do make all nodes unvisited traverse(u, visited) if any unvisited node is still remaining, then return false done return true End
isEularian(ग्राफ)
इनपुट :दिया गया ग्राफ।
आउटपुट:1 देता है, जब यूलरियन सर्किट या पथ, और 0 देता है जब इसमें कोई यूलर पथ नहीं होता है।
Begin if isConnected() is false, then return false define list of degree for each node oddDegree := 0 for all vertex i in the graph, do for all vertex j which are connected with i, do increase degree done if degree of vertex i is odd, then increase oddDegree done if oddDegree > 0, then return 0 else return 1 End
उदाहरण कोड
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#define NODE 5
using namespace std;
int graph[NODE][NODE] = {{0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 0}};
/*int graph[NODE][NODE] = {{0, 1, 1, 1, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 0, 1, 0}};*/ //uncomment to check Euler Circuit as well as path
/*int graph[NODE][NODE] = {{0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 0}};*/ //Uncomment to check Non Eulerian Graph
void traverse(int u, bool visited[]) {
visited[u] = true; //mark v as visited
for(int v = 0; v<NODE; v++) {
if(graph[u][v]) {
if(!visited[v])
traverse(v, visited);
}
}
}
bool isConnected() {
bool *vis = new bool[NODE];
//for all vertex u as start point, check whether all nodes are visible or not
for(int u; u < NODE; u++) {
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++)
vis[i] = false; //initialize as no node is visited
traverse(u, vis);
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++){
if(!vis[i]) //if there is a node, not visited by traversal, graph is not connected
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int isEulerian() {
if(isConnected() == false) //when graph is not connected
return 0;
vector<int> degree(NODE, 0);
int oddDegree = 0;
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j<NODE; j++) {
if(graph[i][j])
degree[i]++; //increase degree, when connected edge found
}
if(degree[i] % 2 != 0) //when degree of vertices are odd
oddDegree++; //count odd degree vertices
}
if(oddDegree > 2) //when vertices with odd degree greater than 2
return 0;
return 1; //when oddDegree is 0, it is Euler circuit, and when 2, it is Euler path
}
int main() {
if(isEulerian() != 0) {
cout << "The graph has Eulerian path." << endl;
} else {
cout << "The graph has No Eulerian path." << endl;
}
} आउटपुट
The graph has Eulerian path.