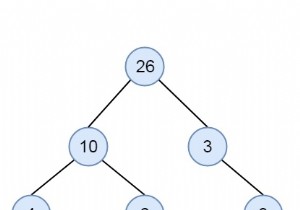
बाइनरी सर्च ट्री एक बाइनरी ट्री डेटा संरचना है जिसमें हमारे पास 3 गुण होते हैं
-
किसी नोड के बाइनरी सर्च ट्री के बाएं उपट्री में केवल नोड की कुंजी से कम कुंजियों वाले नोड होते हैं।
-
बाइनरी सर्च ट्री नोड के दाहिने उपट्री में केवल नोड की कुंजी से बड़ी कुंजियों वाले नोड होते हैं।
-
एक सबट्री के बाएँ और दाएँ पेड़ भी एक बाइनरी सर्च ट्री होना चाहिए।
एल्गोरिदम
Begin function BSTUtill() If node is equals to NULL then Returns 1. If data of node is less than minimum or greater than maximum data then Return 0. Traverse left and right sub-trees recursively. End.
उदाहरण कोड
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <climits>
using namespace std;
struct n {
int d;
n* l;
n* r;
};
int BSTUtil(n* node, int min, int max);
int isBST(n* node) {
return(BSTUtil(node, INT_MIN, INT_MAX));
}
int BSTUtil(struct n* node, int min, int max) {
if (node==NULL)
return 1;
if (node->d < min || node->d > max)
return 0;
return BSTUtil(node->l, min, node->d - 1) && BSTUtil(node->r, node->d + 1, max);
}
n* newN(int d) {
n* nod = new n;
nod->d = d;
nod->l = NULL;
nod->r = NULL;
return nod;
}
int main() {
n *root = newN(7);
root->l = newN(6);
root->r = newN(10);
root->l->l = newN(2);
root->l->r = newN(4);
if (isBST(root))
cout<<"The Given Tree is a BST"<<endl;
else
cout<<"The Given Tree is not a BST"<<endl;
n *root1 = newN(10);
root1->l = newN(6);
root1->r = newN(11);
root1->l->l = newN(2);
root1->l->r = newN(7);
if (isBST(root1))
cout<<"The Given Tree is a BST"<<endl;
else
cout<<"The Given Tree is not a BST"<<endl;
return 0;
} आउटपुट
The Given Tree is not a BST The Given Tree is a BST