AVL ट्री एक सेल्फ-बैलेंसिंग बाइनरी सर्च ट्री है जहां सभी नोड्स के लिए बाएं और दाएं सबट्री की ऊंचाई के बीच का अंतर एक से अधिक नहीं हो सकता है।
यह सेल्फ बैलेंसिंग बाइनरी सर्च ट्री को लागू करने के लिए एक C++ प्रोग्राम है।
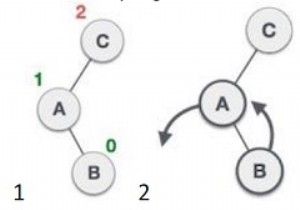
Begin class avl_tree to declare following functions: balance() = Balance the tree by getting balance factor. Put the difference in bal_factor. If bal_factor > 1 then balance the left subtree. If bal_factor < -1 then balance the right subtree. insert() = To insert the elements in the tree: If tree is empty insert data as root. If tree is not empty and data > root Insert data as left child. Else Insert data as right child. End.
उदाहरण कोड
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<sstream>
#include<algorithm>
#define pow2(n) (1 << (n))
using namespace std;
struct avl//node declaration
{
int d;
struct avl *l;
struct avl *r;
}*r;
class avl_tree
{
public://declare functions
int height(avl *);
int difference(avl *);
avl * rr_rotat(avl *);
avl * ll_rotat(avl *);
avl * lr_rotat(avl*);
avl * rl_rotat(avl *);
avl * balance(avl *);
avl * insert(avl *, int);
void show(avl *, int);
void inorder(avl *);
void preorder(avl *);
void postorder(avl*);
avl_tree()
{
r = NULL;
}
};
int avl_tree::height(avl *t)
{
int h = 0;
if (t != NULL)
{
int l_height = height(t→l);
int r_height = height(t→r);
int max_height = max(l_height, r_height);
h = max_height + 1;
}
return h;
}
int avl_tree::difference(avl *t)//calculte difference between left and
right tree
{
int l_height = height(t→l);
int r_height = height(t→r);
int b_factor = l_height - r_height;
return b_factor;
}
avl *avl_tree::rr_rotat(avl *parent)//right right rotation
{
avl *t;
t = parent→r;
parent→r = t→l;
t->l = parent;
cout<<"Right-Right Rotation";
return t;
}
avl *avl_tree::ll_rotat(avl *parent)//left left rotation
{
avl *t;
t = parent→l;
parent→l = t->r;
t->r = parent;
cout<<"Left-Left Rotation";
return t;
}
avl *avl_tree::lr_rotat(avl *parent)//left right rotation
{
avl *t;
t = parent→l;
parent->l = rr_rotat(t);
cout<<"Left-Right Rotation";
return ll_rotat(parent);
}
avl *avl_tree::rl_rotat(avl *parent)//right left rotation
{
avl *t;
t= parent→r;
parent->r = ll_rotat(t);
cout<<"Right-Left Rotation";
return rr_rotat(parent);
}
avl *avl_tree::balance(avl *t)
{
int bal_factor = difference(t);
if (bal_factor > 1)
{
if (difference(t->l) > 0)
t = ll_rotat(t);
else
t = lr_rotat(t);
}
else if (bal_factor < -1)
{
if (difference(t->r) > 0)
t = rl_rotat(t);
else
t = rr_rotat(t);
}
return t;
}
avl *avl_tree::insert(avl *r, int v)
{
if (r == NULL)
{
r = new avl;
r->d = v;
r->l = NULL;
r->r= NULL;
return r;
}
else if (v< r→d)
{
r->l= insert(r→l, v);
r = balance(r);
}
else if (v >= r→d)
{
r->r= insert(r→r, v);
r = balance(r);
}
return r;
}
void avl_tree::show(avl *p, int l)//show the tree
{
int i;
if (p != NULL)
{
show(p->r, l+ 1);
cout<<" ";
if (p == r)
cout << "Root → ";
for (i = 0; i < l&& p != r; i++)
cout << " ";
cout << p→d;
show(p->l, l + 1);
}
}
void avl_tree::inorder(avl *t)//inorder traversal
{
if (t == NULL)
return;
inorder(t->l);
cout << t->d << " ";
inorder(t->r);
}
void avl_tree::preorder(avl *t)//preorder traversal
{
if (t == NULL)
return;
cout << t->d << " ";
preorder(t->l);
preorder(t->r);
}
void avl_tree::postorder(avl *t)//postorder traversal
{
if (t == NULL)
return;
postorder(t ->l);
postorder(t ->r);
cout << t→d << " ";
}
int main()
{
int c, i;
avl_tree avl;
while (1)
{
cout << "1.Insert Element into the tree" << endl;
cout << "2.show Balanced AVL Tree" << endl;
cout << "3.InOrder traversal" << endl;
cout << "4.PreOrder traversal" << endl;
cout << "5.PostOrder traversal" << endl;
cout << "6.Exit" << endl;
cout << "Enter your Choice: ";
cin >> c;
switch ©//perform switch operation
{
case 1:
cout << "Enter value to be inserted: ";
cin >> i;
r= avl.insert(r, i);
break;
case 2:
if (r == NULL)
{
cout << "Tree is Empty" << endl;
continue;
}
cout << "Balanced AVL Tree:" << endl;
avl.show(r, 1);
cout<<endl;
break;
case 3:
cout << "Inorder Traversal:" << endl;
avl.inorder(r);
cout << endl;
break;
case 4:
cout << "Preorder Traversal:" << endl;
avl.preorder(r);
cout << endl;
break;
case 5:
cout << "Postorder Traversal:" << endl;
avl.postorder(r);
cout << endl;
break;
case 6:
exit(1);
break;
default:
cout << "Wrong Choice" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
} आउटपुट
1.Insert Element into the tree 2.show Balanced AVL Tree 3.InOrder traversal 4.PreOrder traversal 5.PostOrder traversal 6.Exit Enter your Choice: 1 Enter value to be inserted: 13 1.Insert Element into the tree 2.show Balanced AVL Tree 3.InOrder traversal 4.PreOrder traversal 5.PostOrder traversal 6.Exit Enter your Choice: 1 Enter value to be inserted: 10 1.Insert Element into the tree 2.show Balanced AVL Tree 3.InOrder traversal 4.PreOrder traversal 5.PostOrder traversal 6.Exit Enter your Choice: 1 Enter value to be inserted: 15 1.Insert Element into the tree 2.show Balanced AVL Tree 3.InOrder traversal 4.PreOrder traversal 5.PostOrder traversal 6.Exit Enter your Choice: 1 Enter value to be inserted: 5 1.Insert Element into the tree 2.show Balanced AVL Tree 3.InOrder traversal 4.PreOrder traversal 5.PostOrder traversal 6.Exit Enter your Choice: 1 Enter value to be inserted: 11 1.Insert Element into the tree 2.show Balanced AVL Tree 3.InOrder traversal 4.PreOrder traversal 5.PostOrder traversal 6.Exit Enter your Choice: 1 Enter value to be inserted: 4 Left-Left Rotation1.Insert Element into the tree 2.show Balanced AVL Tree 3.InOrder traversal 4.PreOrder traversal 5.PostOrder traversal 6.Exit Enter your Choice: 1 Enter value to be inserted: 8 1.Insert Element into the tree 2.show Balanced AVL Tree 3.InOrder traversal 4.PreOrder traversal 5.PostOrder traversal 6.Exit Enter your Choice: 1 Enter value to be inserted: 16 1.Insert Element into the tree 2.show Balanced AVL Tree 3.InOrder traversal 4.PreOrder traversal 5.PostOrder traversal 6.Exit Enter your Choice: 3 Inorder Traversal: 4 5 8 10 11 13 15 16 1.Insert Element into the tree 2.show Balanced AVL Tree 3.InOrder traversal 4.PreOrder traversal 5.PostOrder traversal 6.Exit Enter your Choice: 4 Preorder Traversal: 10 5 4 8 13 11 15 16 1.Insert Element into the tree 2.show Balanced AVL Tree 3.InOrder traversal 4.PreOrder traversal 5.PostOrder traversal 6.Exit Enter your Choice: 5 Postorder Traversal: 4 8 5 11 16 15 13 10 1.Insert Element into the tree 2.show Balanced AVL Tree 3.InOrder traversal 4.PreOrder traversal 5.PostOrder traversal 6.Exit Enter your Choice: 1 Enter value to be inserted: 14 1.Insert Element into the tree 2.show Balanced AVL Tree 3.InOrder traversal 4.PreOrder traversal 5.PostOrder traversal 6.Exit Enter your Choice: 1 Enter value to be inserted: 3 1.Insert Element into the tree 2.show Balanced AVL Tree 3.InOrder traversal 4.PreOrder traversal 5.PostOrder traversal 6.Exit Enter your Choice: 1 Enter value to be inserted: 7 1.Insert Element into the tree 2.show Balanced AVL Tree 3.InOrder traversal 4.PreOrder traversal 5.PostOrder traversal 6.Exit Enter your Choice: 1 Enter value to be inserted: 9 1.Insert Element into the tree 2.show Balanced AVL Tree 3.InOrder traversal 4.PreOrder traversal 5.PostOrder traversal 6.Exit Enter your Choice: 1 Enter value to be inserted: 52 Right-Right Rotation 1.Insert Element into the tree 2.show Balanced AVL Tree 3.InOrder traversal 4.PreOrder traversal 5.PostOrder traversal 6.Exit Enter your Choice: 6