यहाँ हम देखेंगे कि B+ ट्री में इंसर्शन कैसे किया जाता है। मान लीजिए हमारे पास नीचे जैसा B+ ट्री है -
B+ ट्री का उदाहरण -
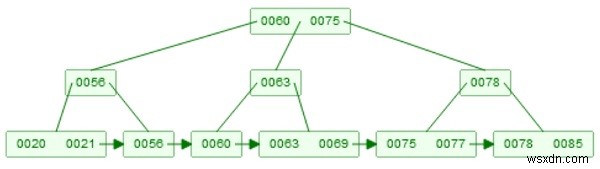
एक तत्व सम्मिलित करने के लिए, विचार बी-ट्री के समान है, यदि एक तत्व डाला जाता है, तो वह लीफ नोड पर संग्रहीत किया जाएगा। अगर वह किसी आंतरिक नोड में मौजूद है, तो वह पत्ते पर अपने आप में सही बच्चे के रूप में भी होगा।
मान लीजिए हम पेड़ में 65 डालना चाहते हैं। तो वह 60 से अधिक है, और 75 से कम है। फिर इसे मध्य उप-वृक्ष में डाला जाएगा। अब, 65, 63 के बाद नोड में डाला जाएगा, फिर उस नोड को दो भागों में विभाजित किया जाएगा, 65 ऊपर जाएगा, और 65 इसके दाहिने नोड पर भी होगा।
B+ ट्री 65 डालने के बाद।
एल्गोरिदम
BPlusTreeInsert(root, key) -
इनपुट -पेड़ की जड़, और डालने की कुंजी
We will assume, that the key is not present into the list Start from root node, perform exact match for key as ‘key’ till a leaf node. Let the search path be x1, x2, … , xh. The x1 is first node so root, then xh is leaf node. Each node xi is parent of xi+1 Insert the new object where key is ‘key’, and value is v into xh. i := h while xi overflows, do divide xi into two nodes, by moving the larger half of the keys into a new node p. if xi is leaf node, link p into the linked list among leaf nodes. identify a key k, to be inserted into the parent level along with child pointer pointing p. The choice of k depends on the type of the node xi. If xi is leaf node, we will perform copy up. So smallest key in p, is copied as k to the parent level. On the other hand, if xi is non-leaf node, then we will perform push up. So smallest key in p, will be copied into k, in the parent node. if i = 0, then create a new index node as the new root. In the new root store node with key k, and two child xi and p. return else insert a key k and a child pointer pointing to p, into node xi-1. i := i – 1 end if done