यहां हम देखेंगे कि B+ ट्री से किसी नोड को कैसे हटाया जाए। मान लीजिए हमारे पास 7minus से नीचे जैसा B+ ट्री है;
B+ ट्री का उदाहरण -
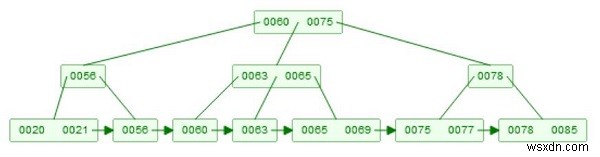
विलोपन के दो भाग होते हैं। सबसे पहले हमें तत्व को खोजना होगा। वह रणनीति पूछताछ की तरह है। अब डिलीट करने के लिए हमें कुछ नियमों का ध्यान रखना होगा। एक नोड में कम से कम m/2 तत्व होने चाहिए। इसलिए यदि हम एक तत्व को हटाते हैं, और इसमें m-1 से कम तत्व शेष हैं, तो यह अपने आप समायोजित हो जाएगा। यदि पूरा नोड हटा दिया जाता है, तो उसके बच्चे मर्ज हो जाएंगे, और यदि उनका आकार m के समान है, तो उन्हें दो भागों में विभाजित करें, और फिर से माध्य मान बढ़ जाएगा।
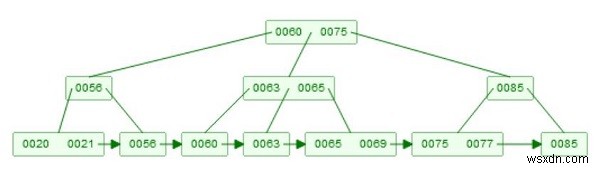
मान लीजिए हम 78 हटाना चाहते हैं। अब दो बच्चे हैं। [75, 77], और [78, 85], फिर यह पहले लीफ नोड से 78 हटाएगा, उसके बाद 85 लेगा, और कुंजी 85 की एक प्रति बनाएगा, और इसे सबट्री की जड़ के रूप में बनाएगा।
एल्गोरिदम
BPlusTreeDelete(x, key) -
इनपुट - पेड़ की जड़, और हटाने की कुंजी
We will assume, that the key is present into the list Start from root node, perform exact match for key as ‘key’ till a leaf node. Let the search path be x1, x2, … , xh. The x1 is first node so root, then xh is leaf node. Each node xi is parent of xi+1 delete the object where key is ‘key’ from xh. if h = 1, then return, as there is only one node which is root. i := h while xi underflows, do if immediate sibling node s of xi, has at least m/2 + 1 elements, then redistribute entries evenly between s and xi. corresponding to redistribution, a key k in the parent node xi-1, will be changed. if xi is non-leaf node, then k is dragged down to xi. and a key from s is pushed up to fill the place of k else k is simply replaced by a key in s return else merge xi with the sibling node s. Delete the corresponding child pointer in xi-1. if xi is an internal node, then drag the key in xi-1. which is previously divides xi and s. into the new node xi and s, into the new node xi. else delete that key in xi-1. i := i – 1 end if done