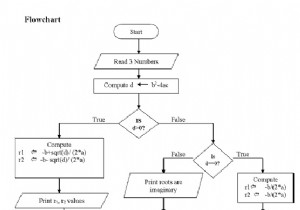
द्विघात समीकरण ax 2 . के रूप में होता है + बीएक्स + सी। द्विघात समीकरण के मूल निम्न सूत्र द्वारा दिए गए हैं -

तीन मामले हैं -
बी 2 <4*a*c - जड़ें असली नहीं होती हैं यानी वे जटिल होती हैं
बी 2 =4*a*c - मूल वास्तविक हैं और दोनों मूल समान हैं।
बी 2 > 4*a*c - जड़ें असली हैं और दोनों जड़ें अलग हैं
द्विघात समीकरण के मूल ज्ञात करने का कार्यक्रम इस प्रकार दिया गया है।
उदाहरण
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a = 1, b = 2, c = 1;
float discriminant, realPart, imaginaryPart, x1, x2;
if (a == 0) {
cout << "This is not a quadratic equation";
}else {
discriminant = b*b - 4*a*c;
if (discriminant > 0) {
x1 = (-b + sqrt(discriminant)) / (2*a);
x2 = (-b - sqrt(discriminant)) / (2*a);
cout << "Roots are real and different." << endl;
cout << "Root 1 = " << x1 << endl;
cout << "Root 2 = " << x2 << endl;
} else if (discriminant == 0) {
cout << "Roots are real and same." << endl;
x1 = (-b + sqrt(discriminant)) / (2*a);
cout << "Root 1 = Root 2 =" << x1 << endl;
}else {
realPart = (float) -b/(2*a);
imaginaryPart =sqrt(-discriminant)/(2*a);
cout << "Roots are complex and different." << endl;
cout << "Root 1 = " << realPart << " + " << imaginaryPart << "i" <<end;
cout << "Root 2 = " << realPart << " - " << imaginaryPart << "i" <<end;
}
}
return 0;
} आउटपुट
Roots are real and same. Root 1 = Root 2 =-1
उपरोक्त कार्यक्रम में, पहले विवेचक की गणना की जाती है। यदि यह 0 से बड़ा है, तो दोनों मूल वास्तविक और भिन्न हैं।
यह निम्नलिखित कोड स्निपेट द्वारा प्रदर्शित किया जाता है।
if (discriminant > 0) {
x1 = (-b + sqrt(discriminant)) / (2*a);
x2 = (-b - sqrt(discriminant)) / (2*a);
cout << "Roots are real and different." << endl;
cout << "Root 1 = " << x1 << endl;
cout << "Root 2 = " << x2 << endl;
} यदि विवेचक 0 के बराबर है, तो दोनों मूल वास्तविक और समान हैं। यह निम्नलिखित कोड स्निपेट द्वारा प्रदर्शित किया जाता है।
else if (discriminant == 0) {
cout << "Roots are real and same." << endl;
x1 = (-b + sqrt(discriminant)) / (2*a);
cout << "Root 1 = Root 2 =" << x1 << endl;
} यदि विवेचक 0 से कम है, तो दोनों मूल जटिल और भिन्न हैं। यह निम्नलिखित कोड स्निपेट द्वारा प्रदर्शित किया जाता है।
else {
realPart = (float) -b/(2*a);
imaginaryPart =sqrt(-discriminant)/(2*a);
cout << "Roots are complex and different." << endl;
cout << "Root 1 = " << realPart << " + " << imaginaryPart << "i" << endl;
cout << "Root 2 = " << realPart << " - " << imaginaryPart << "i" << endl;
}