अप्रत्यक्ष ग्राफ़ के लिए, शीर्ष आवरण शीर्षों का एक उपसमुच्चय होता है, जहां ग्राफ़ के प्रत्येक किनारे (u, v) के लिए या तो u या v सेट में होता है।
बाइनरी ट्री का उपयोग करके, हम आसानी से वर्टेक्स कवर की समस्या को हल कर सकते हैं।
इस समस्या को दो उप-समस्याओं में विभाजित किया जा सकता है। जब जड़ शीर्ष आवरण का भाग हो। इस मामले में, जड़ सभी बच्चों के किनारों को कवर करती है। हम बस बाएं और दाएं उप-वृक्ष के लिए शीर्ष आवरण का आकार ढूंढ सकते हैं, और जड़ के लिए 1 जोड़ सकते हैं।
इनपुट और आउटपुट
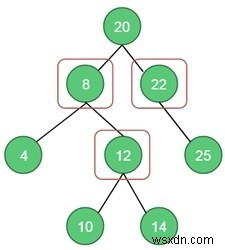
Input: A binary tree.Output: The vertex cover is 3.
एल्गोरिदम
vertexCover(root node)
इस समस्या में, एक बाइनरी ट्री बनेगा, प्रत्येक नोड डेटा और उस नोड द्वारा कवर किए गए शीर्षों की संख्या रखेगा।
इनपुट - बाइनरी ट्री की जड़।
आउटपुट - जड़ से आच्छादित शीर्षों की संख्या।
Begin if root is φ, then return 0 if root has no child, then return 0 if vCover(root) ≠ 0, then return vCover(root) withRoot := 1 + vertexCover(left(root)) + vertexCover(right(root)) withoutRoot := 0 if root has left child, then withoutRoot := withoutRoot + vertexCover(left(left(root))) + vertexCover(left(right(root))) if root has right child, then withoutRoot := withoutRoot + vertexCover(right(left(root))) + vertexCover(right(right(root))) return vCover(root) End
उदाहरण
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
int vCover;
node *left, *right;
};
node *getNode(int data) {
node *newNode = new (node);
newNode->data = data;
newNode->vCover = 0; //set vertex cover to 0
newNode->left = NULL;
newNode->right = NULL;
return newNode; //newly created node
}
int vertexCover(node *root) {
if(root == NULL) //when tree is empty
return 0;
if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) //when no other edge from root
return 0;
if(root->vCover != 0) //when vertex cover of this node is found, leave that node
return root->vCover;
int sizeWithRoot = 1 + vertexCover(root->left) + vertexCover(root->right);
int sizeWithOutRoot = 0;
if(root->left != NULL) //when root is not included and go for left child
sizeWithOutRoot += 1 + vertexCover(root->left->left) + vertexCover(root->left->right);
if(root->right != NULL) //when root is not included and go for right child
sizeWithOutRoot += 1 + vertexCover(root->right->left) + vertexCover(root->right->right);
root->vCover = (sizeWithRoot < sizeWithOutRoot)?sizeWithRoot:sizeWithOutRoot; //minimum vertex cover
return root->vCover;
}
int main() {
//create tree to check vertex cover
node *root = getNode(20);
root->left = getNode(8); root->right = getNode(22);
root->left->left = getNode(4); root->left->right = getNode(12);
root->left->right->left = getNode(10); root->left->right->right = getNode(14);
root->right->right = getNode(25);
cout << "Minimal vertex cover: " << vertexCover(root);
} आउटपुट
Minimal vertex cover: 3