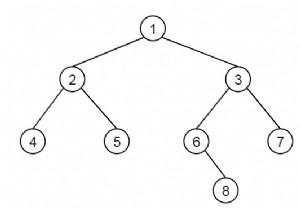
एक बाइनरी ट्री जिसमें अधिकतम दो बच्चे होते हैं, जिसे बाएं बच्चे और दाएं बच्चे के रूप में निर्दिष्ट किया जाता है। यह बाइनरी ट्री में सबसे गहरा बायां पत्ता खोजने के लिए C++ प्रोग्राम है
एल्गोरिदम
Begin. function deepestLLeafutil() find the deepest left leaf in a given binary tree: lvel is level of current node. maxlvel is pointer to the deepest left leaf node found so far isLeft Indicates that this node is left child of its parent resPtr is Pointer to the result If root is equal to Null then Return. Update result if this node is having a left leaf and its level is more than the max level of the current result. Recursively call function deepestLLeafutil() for left and right subtrees. End.
उदाहरण कोड
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct n {
int v;
n *l, *r;
};
void deepestLLeafutil(n *root, int lvel, int *maxvel, bool isLeft, n **resPtr) {
if (root == NULL)
return;
if (isLeft && !root->l && !root->r && lvel > *maxvel) {
*resPtr = root;
*maxvel = lvel;
return;
}
deepestLLeafutil(root->l, lvel + 1, maxvel, true, resPtr);
deepestLLeafutil(root->r, lvel + 1, maxvel, false, resPtr);
}
n* deepestLLeaf( n *root) {
int maxlevel = 0;
n *res = NULL;
deepestLLeafutil(root, 0, &maxlevel, false, &res);
return res;
}
n *newnode(int d) {
n *t = new n;
t->v = d;
t->l = t->r = NULL;
return t;
}
int main() {
n* root = newnode(9);
root->l = newnode(7);
root->r = newnode(10);
root->l->l = newnode(6);
root->r->l= newnode(8);
root->r->r = newnode(19);
root->r->l->r = newnode(4);
root->r->r->r = newnode(20);
n *res = deepestLLeaf(root);
if (res)
cout << "The deepest left leaf is " << res->v;
else
cout << "There is no left leaf in the given tree";
return 0;
} आउटपुट
The deepest left leaf is 6