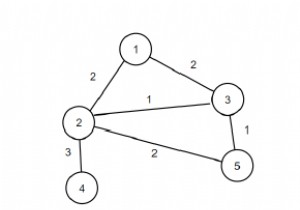
इस कार्यक्रम में हम मूल रूप से एक फीडबैक आर्क सेट पाएंगे जिसमें किनारों को शामिल किया गया है, जिसे ग्राफ से हटा दिए जाने पर, ग्राफ निर्देशित एसाइक्लिक ग्राफ बन जाता है।
एल्गोरिदम
Begin function checkCG(int n) : n: number of vertices. arr: struct graph variable. Initialize cnt = 0 and size = (n-1). For i = 0 to n-1 if (cnt == size) return 0 if (arr[i].ptr == NULL) Increase cnt. for j = 0 to n-1 while (arr[j].ptr != NULL) if ((arr[j].ptr)->des == (arr[i].ptr)->des) (arr[j].ptr)->des = -1 arr[i].ptr = (arr[i].ptr)->next Done Done Done Done initialize visited[n + 1] For i = 0 to n-1 while (arr[i].ptr != NULL) Print (arr[i].ptr)->des visited[i] = 1 for j = 0 to n-1 while (arr[j].ptr != NULL) print (arr[j].ptr)->des if (visited[arr[j].v] == 1) print arr[i].v << " - " << arr[j].v Done arr[j].ptr = (arr[j].ptr)->next Done Done arr[i].ptr = (arr[i].ptr)->next Done Done return 1 End
उदाहरण
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int c = 0;
struct ad_list {
int des;
ad_list *next;
}*np = NULL, *np1 = NULL, *p = NULL, *q = NULL;
struct Graph {
int v;
ad_list *ptr;
} array[6];
void addRevEdge(int sr, int des) //to add reverse edge in the graph {
np1 = new ad_list;
np1->des = sr;
np1->next = NULL;
if (arr[des].ptr == NULL) {
arr[des].ptr = np1;
q = arr[des].ptr;
q->next = NULL;
} else {
q = arr[des].ptr;
while (q->next != NULL) {
q = q->next;
}
q->next = np1;
}
}
void addEd(int sr, int des) // to add edge in the graph {
np = new ad_list;
np->des = des;
np->next = NULL;
if (arr[sr].ptr == NULL) {
arr[sr].ptr = np;
p = arr[sr].ptr;
p->next = NULL;
} else {
p = arr[sr].ptr;
while (p->next != NULL) {
p = p->next;
}
p->next = np;
}
}
void print_graph(int n) //to print graph {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << "Adjacency List of " << arr[i].v << ": ";
while (arr[i].ptr != NULL) {
cout << (arr[i].ptr)->des << " ";
arr[i].ptr = (arr[i].ptr)->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
//to check whether the graph is directed acyclic graph or not.
int checkCG(int n) {
int cnt = 0;
int size = n - 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (cnt == size) {
return 0;
}
if (arr[i].ptr == NULL) {
cnt++;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
while (arr[j].ptr != NULL) {
if ((arr[j].ptr)->des == (arr[i].ptr)->des) {
(arr[j].ptr)->des = -1;
}
arr[i].ptr = (arr[i].ptr)->next;
}
}
}
}
cout<<"after checking dag";
int visited[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (arr[i].ptr != NULL) {
cout << (arr[i].ptr)->des << " ";
visited[i] = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
while (arr[j].ptr != NULL) {
cout << (arr[j].ptr)->des << " ";
if (visited[arr[j].v] == 1) {
cout << arr[i].v << " - " << arr[j].v;
}
arr[j].ptr = (arr[j].ptr)->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
arr[i].ptr = (arr[i].ptr)->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
return 1;
}
int main() {
int n = 5;
cout << "Number of vertices: " << n << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i].v = i;
arr[i].ptr = NULL;
}
addEd(1, 2);
addEd(2, 1);
addEd(0, 1);
addEd(2, 3);
addEd(2, 0);
addEd(5, 4);
addEd(4, 2);
print_graph(n);
cout << "Feedback arc Set: ";
if (checkCG(n) == 0)
cout << " None";
} आउटपुट
Number of vertices: 5 Adjacency List of 0: 1 Adjacency List of 1: 2 Adjacency List of 2: 1 3 0 Adjacency List of 3: Adjacency List of 4: 2 Feedback arc Set: None