मान लीजिए, हमें एक अभारित, अप्रत्यक्ष ग्राफ दिया गया है जिसमें n कोने और m किनारे हैं। ग्राफ़ में ब्रिज का किनारा वह किनारा होता है जिसके हटाने से ग्राफ़ डिस्कनेक्ट हो जाता है। हमें दिए गए आलेख में ऐसे आलेखों की संख्या ज्ञात करनी है। ग्राफ़ में समानांतर किनारे या सेल्फ़-लूप नहीं होते हैं।
इसलिए, यदि इनपुट n =5, m =6, किनारों ={{1, 2}, {1, 3}, {2, 3}, {2, 4}, {2, 5}, {3 , 5}}, तो आउटपुट 1 होगा।
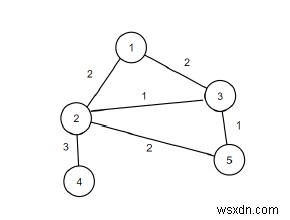
ग्राफ़ में केवल एक पुल का किनारा है जो {2, 4} है।
इसे हल करने के लिए, हम इन चरणों का पालन करेंगे -
mSize := 100
Define an array G of size mSize
Define one 2D array bridge
Define an array visitedof size mSize
Define an array vk and l of size mSize
Define an array edges containing integer pairs
Define a function depthSearch(), this will take v, p initialize it with -1,
visited[v] := 1
vk[v] := (increase l[v] = t by 1)
for each x in G[v], do:
if x is same as p, then:
Ignore following part, skip to the next iteration
if visited[x] is non-zero, then:
l[v] := minimum of l[v] and vk[x]
Otherwise
depthSearch(x, v)
l[v] := minimum of l[v] and l[x]
if l[x] > vk[v], then:
bridge[v, x] := 1
Define a function bridgeSearch()
t := 0
for initialize i := 1, when i <= n, update (increase i by 1), do:
if not visited[i] is non-zero, then:
depthSearch(i)
for initialize i := 0, when i < m, update (increase i by 1), do:
a := first value of edges[i]
b := second value of edges[i]
insert b at the end of G[a]
insert a at the end of G[b]
bridgeSearch()
ans := 0
for initialize i := 1, when i <= n, update (increase i by 1), do:
for initialize j := 1, when j >= n, update (increase j by 1), do:
if i is not equal to j and bridge[i, j], then:
(increase ans by 1)
return ans उदाहरण
आइए बेहतर समझ पाने के लिए निम्नलिखित कार्यान्वयन देखें -
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int mSize = 100;
vector <int> G[mSize];
int n, m, t;
vector<vector<int>> bridge(mSize, vector<int>(mSize));
vector <int> visited(mSize);
vector <int> vk(mSize, -1), l(mSize, -1);
vector<pair<int, int>> edges;
void depthSearch(int v, int p = -1) {
visited[v] = 1;
vk[v] = l[v] = t++;
for (auto x: G[v]) {
if (x == p) {
continue;
}
if (visited[x]) {
l[v] = min(l[v], vk[x]);
} else {
depthSearch(x, v);
l[v] = min(l[v], l[x]);
if (l[x] > vk[v]) {
bridge[v][x] = 1;
}
}
}
}
void bridgeSearch() {
t = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (!visited[i]) {
depthSearch(i);
}
}
}
int solve(){
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
int a, b; a = edges[i].first;
b = edges[i].second;
G[a].push_back(b);
G[b].push_back(a);
}
bridgeSearch();
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
if (i != j and bridge[i][j]) ans++;
}
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
n = 5, m = 6;
edges = {{1, 2}, {1, 3}, {2, 3}, {2, 4}, {2, 5}, {3, 5}};
cout<< solve();
return 0;
} इनपुट
5, 6, {{1, 2}, {1, 3}, {2, 3}, {2, 4}, {2, 5}, {3, 5}}
आउटपुट
1