मान लीजिए, हमें दो पूर्णांक n और m दिए गए हैं और पूर्णांकों के k टुपल्स हैं जिनमें चार पूर्णांक संख्याएँ {ai, bi, ci, di} हैं। चार सरणियाँ a, b, c, d दिए गए हैं, और a[i] i-th tuple के मान को दर्शाता है। अब, आइए एक अनुक्रम dp पर विचार करें जिसमें n धनात्मक पूर्णांक हैं और 1 <=dp[1]
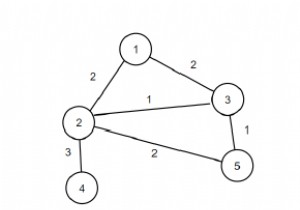
इसलिए, यदि इनपुट n =4, m =5, k =4, a ={2, 2, 3, 5}, b ={4, 3, 4, 6}, c ={4, 3, 3, 4}, d ={110, 20, 20, 40}, तो आउटपुट 130 होगा।
इसे हल करने के लिए, हम इन चरणों का पालन करेंगे -
आइए बेहतर समझ पाने के लिए निम्नलिखित कार्यान्वयन देखें -कदम
Define arrays A, B, C, D, and dp of sizes: 100, 100, 100, 100, 10 respectively.
Define a function depthSearch(), this will take c, l,
if c is same as n, then:
total := 0
for initialize i := 0, when i < k, update (increase i by 1), do:
if dp[B[i]] - dp[A[i]] is same as C[i], then:
total := total + D[i]
res := maximum of res and total
return
for initialize j := l, when j <= m, update (increase j by 1), do:
dp[c] := j
depthSearch(c + 1, j)
for initialize i := 0, when i < k, update (increase i by 1), do:
A[i] := a[i], B[i] := b[i], C[i] := c[i], D[i] := d[i]
decrease A[i] by 1
decrease B[i] by 1
depthSearch(0, 1)
return res
उदाहरण
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n, m, k, res = 0;
int A[100], B[100], C[100], D[100], dp[10];
void depthSearch(int c, int l){
if(c == n){
int total = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
if(dp[B[i]] - dp[A[i]] == C[i]) total += D[i];
}
res = max(res, total);
return;
}
for(int j = l; j <= m; j++){
dp[c] = j;
depthSearch(c + 1, j);
}
}
int solve(int a[], int b[], int c[], int d[]){
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){
A[i] = a[i], B[i] = b[i], C[i] = c[i], D[i] = d[i]; A[i]--, B[i]--;
}
depthSearch(0, 1);
return res;
}
int main() {
n = 4, m = 5, k = 4;
int a[] = {2, 2, 3, 5}, b[] = {4, 3, 4, 6}, c[] = {4, 3, 3, 4}, d[] = {110, 20, 20, 40};
cout<< solve(a, b, c, d);
return 0;
} इनपुट
4, 5, 4, {2, 2, 3, 5}, {4, 3, 4, 6}, {4, 3, 3, 4}, {110, 20, 20, 40}
आउटपुट
130