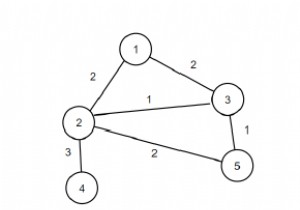
मान लीजिए, हमारे पास पूर्णांक 'seq' का क्रमचय और m आकार के पूर्णांक जोड़े 'जोड़े' की एक सरणी है जिसमें पूर्णांक 0 से n-1 है। i] =i (0 ≤ i
हमें एक पूर्णांक j चुनना होगा जहां 0 <=j
हमें i का अधिकतम मान ज्ञात करना है ताकि seq[i] =i कई बार ऑपरेशन करने के बाद।
इसलिए, यदि इनपुट n =4, m =2, seq ={0, 3, 2, 1}, जोड़े ={{0, 1}, {2, 3}} जैसा है, तो आउटपुट 2 होगा।
अधिकतम संभव मान 2 है।
इसे हल करने के लिए, हम इन चरणों का पालन करेंगे -
आइए बेहतर समझ पाने के लिए निम्नलिखित कार्यान्वयन देखें -
N := 100
Define an array tp of size: N.
Define arrays vtmp, vis of size N.
Define a function dfs(), this will take j, k,
tp[j] := k
insert j at the end of vtmp[k]
for each value b in vis[j], do:
if tp[b] is not equal to 0, then:
Ignore following part, skip to the next iteration
dfs(b, k)
res := 0
for initialize i := 0, when i < n, update (increase i by 1), do:
if seq[i] is same as i, then:
(increase res by 1)
for initialize i := 0, when i < m, update (increase i by 1), do:
a := first value of pairs[i]
b := second value of pairs[i]
insert b at the end of vis[a]
insert a at the end of vis[b]
idx := 1
for initialize i := 0, when i < n, update (increase i by 1), do:
if tp[i] is same as 0, then:
dfs(i, idx)
for each element j in vtmp[idx], do:
if tp[seq[j]] is same as idx and seq[j] is not equal to j, then:
(increase res by 1)
(increase idx by 1)
print(res)
उदाहरण
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int INF = 1e9;
#define N 100
int tp[N];
vector<int> vtmp[N], vis[N];
void dfs(int j, int k){
tp[j] = k;
vtmp[k].push_back(j);
for(auto b : vis[j]) {
if(tp[b] != 0)
continue;
dfs(b, k);
}
}
void solve(int n, int m, int seq[], vector<pair<int, int>> pairs) {
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(seq[i] == i)
res++;
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
int a = pairs[i].first;
int b = pairs[i].second;
vis[a].push_back(b);
vis[b].push_back(a);
}
int idx = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(tp[i] == 0) {
dfs(i, idx);
for(auto j: vtmp[idx]){
if(tp[seq[j]] == idx && seq[j] != j)
res++;
}
idx++;
}
}
cout<< res;
}
int main() {
int n = 4, m = 2, seq[] = {0, 3, 2, 1};
vector<pair<int,int>> pairs = {{0, 1}, {2, 3}};
solve(n, m, seq, pairs);
return 0;
} इनपुट
4, 2, {0, 3, 2, 1}, {{0, 1}, {2, 3}} आउटपुट
2