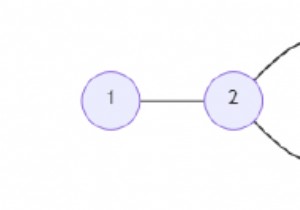
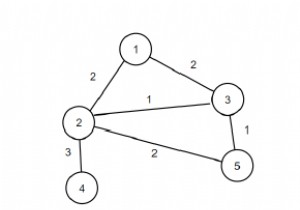
इस कार्यक्रम में हमें एक ग्राफ की एज कनेक्टिविटी को खोजने की जरूरत है। ग्राफ़ के ग्राफ़ की एक एज कनेक्टिविटी का अर्थ है कि यह एक पुल है, इसे हटाने से ग्राफ़ डिस्कनेक्ट हो जाएगा। डिस्कनेक्ट किए गए अप्रत्यक्ष ग्राफ़ में पुल को हटाने के साथ जुड़े घटकों की संख्या बढ़ जाती है।
कार्य और छद्म कोड
Begin Function connections() is a recursive function to find out the connections: A) Mark the current node un visited. B) Initialize time and low value C) Go through all vertices adjacent to this D) Check if the subtree rooted with x has a connection to one of the ancestors of w. If the lowest vertex reachable from subtree under x is below u in DFS tree, then w-x has a connection. E) Update low value of w for parent function calls. End
कोन के कार्य और छद्म कोड ()
Begin Function Con() that uses connections(): A) Mark all the vertices as unvisited. B) Initialize par and visited, and connections. C) Print the connections between the edges in the graph. End
उदाहरण
#include<iostream>
#include <list>
#define N -1
using namespace std;
class G
{
//declaration of functions
int n;
list<int> *adj;
void connections(int n, bool visited[], int disc[], int
low[],
int par[]);
public:
G(int n); //constructor
void addEd(int w, int x);
void Con();
};
G::G(int n)
{
this->n= n;
adj = new list<int> [n];
}
//add edges to the graph
void G::addEd(int w, int x)
{
adj[x].push_back(w); //add u to v's list
adj[w].push_back(x); //add v to u's list
}
void G::connections(int w, bool visited[], int dis[], int low[],
int par[])
{
static int t = 0;
//mark current node as visited
visited[w] = true;
dis[w] = low[w] = ++t;
//Go through all adjacent vertices
list<int>::iterator i;
for (i = adj[w].begin(); i != adj[w].end(); ++i) {
int x = *i; //x is current adjacent
if (!visited[x]) {
par[x] = w;
connections(x, visited, dis, low, par);
low[w] = min(low[w], low[x]);
// If the lowest vertex reachable from subtree under x is
below w in DFS tree, then w-x is a connection
if (low[x] > dis[w])
cout << w << " " << x << endl;
}
else if (x != par[w])
low[w] = min(low[w], dis[x]);
}
}
void G::Con()
{
// Mark all the vertices as unvisited
bool *visited = new bool[n];
int *dis = new int[n];
int *low = new int[n];
int *par = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
par[i] = N;
visited[i] = false;
}
//call the function connections() to find edge
connections
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (visited[i] == false)
connections(i, visited, dis, low, par);
}
int main()
{
cout << "\nConnections in first graph \n";
G g1(5);
g1.addEd(1, 2);
g1.addEd(3, 2);
g1.addEd(2, 1);
g1.addEd(0, 1);
g1.addEd(1, 4);
g1.Con();
return 0;
} आउटपुट
Connections in first graph 2 3 1 2 1 4 0 1