मान लीजिए, हमारे पास h x w आयामों का एक ग्रिड है। ग्रिड को 'इनिटग्रिड' नामक 2डी सरणी में दर्शाया जाता है, जहां ग्रिड में प्रत्येक सेल को या तो '#' या '.' द्वारा दर्शाया जाता है। '#' का अर्थ है कि ग्रिड में एक बाधा है और '.' इसका मतलब है कि उस सेल के माध्यम से एक रास्ता है। अब, पंक्ति संख्या x और स्तंभ संख्या y वाले ग्रिड पर सेल 'c' पर एक रोबोट रखा गया है। रोबोट को पंक्ति संख्या p और स्तंभ संख्या q वाले दूसरे सेल 'd' में जाना होता है। दोनों सेल निर्देशांक c और d को पूर्णांक जोड़े के रूप में हमारे सामने प्रस्तुत करते हैं। अब, रोबोट निम्नलिखित तरीकों से एक सेल से दूसरे सेल में जा सकता है -
-
रोबोट केवल एक सेल से दूसरे सेल में चल सकता है यदि वह जिस सेल में जाना चाहता है वह उस सेल के लंबवत या क्षैतिज रूप से स्थित है जिसमें वह वर्तमान में है।
-
रोबोट 5×5 क्षेत्र के किसी भी सेल में जा सकता है, जिसका केंद्र उस सेल में है जो वर्तमान में स्थित है।
-
रोबोट ग्रिड में किसी अन्य सेल में तभी जा सकता है जब गंतव्य सेल में कोई बाधा न हो। रोबोट भी ग्रिड नहीं छोड़ सकता।
हमें यह पता लगाना होगा कि गंतव्य तक पहुंचने के लिए कितनी छलांग लगानी होगी।
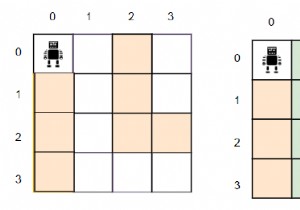
इसलिए, यदि इनपुट h =4, w =4, c ={2, 1}, d ={4, 4}, initGrid ={"#...", ".##.", ". ..#", "..#"}, तो आउटपुट 1 होगा। रोबोट को अपने गंतव्य तक पहुंचने के लिए केवल एक छलांग की आवश्यकता होगी।
इसे हल करने के लिए, हम इन चरणों का पालन करेंगे -
N:= 100
Define intger pairs s and t.
Define an array grid of size: N.
Define an array dst of size: N x N.
Define a struct node that contains integer values a, b, and e.
Define a function check(), this will take a, b,
return a >= 0 AND a < h AND b >= 0 AND b < w
Define a function bfs(), this will take a, b,
for initialize i := 0, when i < h, update (increase i by 1), do:
for initialize j := 0, when j < w, update (increase j by 1), do:
dst[i, j] := infinity
dst[a, b] := 0
Define one deque doubleq
Insert a node containing values {a, b, and dst[a, b]} at the end of doubleq
while (not doubleq is empty), do:
nd := first element of doubleq
if e value of nd > dst[a value of nd, b value of nd], then:
Ignore the following part, skip to the next iteration
for initialize diffx := -2, when diffx <= 2, update (increase diffx by 1), do:
for initialize diffy := -2, when diffy <= 2, update (increase diffy by 1), do:
tm := |diffx + |diffy||
nx := a value of nd + diffx, ny = b value of nd + diffy
if check(nx, ny) and grid[nx, ny] is same as '.', then:
w := (if tm > 1, then 1, otherwise 0)
if dst[a value of nd, b value of nd] + w < dst[nx, ny], then:
dst[nx, ny] := dst[a value of nd, b value of nd] + w
if w is same as 0, then:
insert node containing values ({nx, ny, dst[nx, ny]}) at the beginning of doubleq.
Otherwise
insert node containing values ({nx, ny, dst[nx, ny]}) at the end of doubleq.
s := c
t := d
(decrease first value of s by 1)
(decrease second value of s by 1)
(decrease first value of t by 1)
(decrease second value of t by 1)
for initialize i := 0, when i < h, update (increase i by 1), do:
grid[i] := initGrid[i]
bfs(first value of s, second value of s)
print(if dst[first value of t, second value of t] is same as infinity, then -1, otherwise dst[first value of t, second value of t]) उदाहरण
आइए बेहतर समझ पाने के लिए निम्नलिखित कार्यान्वयन देखें -
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int INF = 1e9;
#define N 100
int h, w;
pair<int, int> s, t;
string grid[N];
int dst[N][N];
struct node {
int a, b, e;
};
bool check(int a, int b) {
return a >= 0 && a < h && b >= 0 && b < w;
}
void bfs(int a, int b) {
for (int i = 0; i < h; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < w; j++)
dst[i][j] = INF;
}
dst[a][b] = 0;
deque<node> doubleq;
doubleq.push_back({a, b, dst[a][b]});
while (!doubleq.empty()) {
node nd = doubleq.front();
doubleq.pop_front();
if (nd.e > dst[nd.a][nd.b])
continue;
for (int diffx = -2; diffx <= 2; diffx++) {
for (int diffy = -2; diffy <= 2; diffy++) {
int tm = abs(diffx) + abs(diffy);
int nx = nd.a + diffx, ny = nd.b + diffy;
if (check(nx, ny) && grid[nx][ny] == '.') {
int w = (tm > 1) ? 1 : 0;
if (dst[nd.a][nd.b] + w < dst[nx][ny]) {
dst[nx][ny] = dst[nd.a][nd.b] + w;
if (w == 0)
doubleq.push_front({nx, ny, dst[nx][ny]});
else
doubleq.push_back({nx, ny, dst[nx][ny]});
}
}
}
}
}
}
void solve(pair<int,int> c, pair<int, int> d, string initGrid[]){
s = c;
t = d;
s.first--, s.second--, t.first--, t.second--;
for(int i = 0; i < h; i++)
grid[i] = initGrid[i];
bfs(s.first, s.second);
cout << (dst[t.first][t.second] == INF ? -1 :
dst[t.first][t.second]) << '\n';
}
int main() {
h = 4, w = 4;
pair<int,int> c = {2, 1}, d = {4, 4};
string initGrid[] = {"#...", ".##.", "...#", "..#."};
solve(c, d, initGrid);
return 0;
} इनपुट
4, 4, {2, 1}, {4, 4}, {"#...", ".##.", "...#", "..#."} आउटपुट
1