कार्य किसी दिए गए बाइनरी ट्री के बाएं नोड्स को प्रिंट करना है। सबसे पहले उपयोगकर्ता डेटा सम्मिलित करेगा इसलिए बाइनरी ट्री उत्पन्न करेगा और इस प्रकार बने ट्री के बाएं दृश्य को प्रिंट करेगा।
प्रत्येक नोड में अधिकतम 2 बच्चे हो सकते हैं, इसलिए यहां प्रोग्राम को नोड से जुड़े केवल बाएं पॉइंटर को पार करना चाहिए
यदि लेफ्ट पॉइंटर शून्य नहीं है, तो इसका मतलब है कि इसके साथ कुछ डेटा या पॉइंटर जुड़ा होगा यदि नहीं तो यह लेफ्ट चाइल्ड होगा जिसे प्रिंट किया जाएगा और आउटपुट के रूप में प्रदर्शित किया जाएगा।
उदाहरण
Input : 1 0 3 2 4 Output : 1 0 2
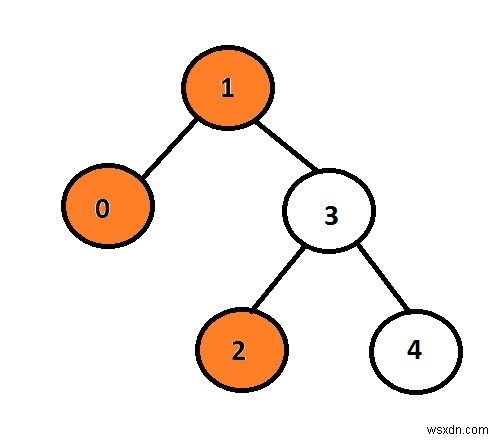
यहाँ, नारंगी नोड बाइनरी ट्री के बाएँ दृश्य का प्रतिनिधित्व करते हैं।
दिए गए आंकड़े में डेटा 1 के साथ नोड एक रूट नोड है, इसलिए इसे बाएं बच्चे के पास जाने से प्रिंट किया जाएगा, यह 0 प्रिंट करेगा और इससे 3 गोटो होगा और इसके बाएं बच्चे को प्रिंट करेगा जो कि 2 है।
हम नोड के स्तर को संग्रहीत करने और बार-बार दूसरे में स्थानांतरित करने के लिए पुनरावर्ती दृष्टिकोण का उपयोग कर सकते हैं।
नीचे दिया गया कोड दिए गए एल्गोरिथम के c कार्यान्वयन को दर्शाता है
एल्गोरिदम
START Step 1 -> create node variable of type structure Declare int data Declare pointer of type node using *left, *right Step 2 -> create function for inserting node with parameter as new_data Declare temp variable of node using malloc Set temp->data = new_data Set temp->left = temp->right = NULL return temp Step 3 -> declare function void left_view(struct node* root, int level, int* highest_level) IF root = NULL Exit End IF *highest_level < level Print root->data Set *highest_level = level End Recursively call left_view(root->left, level + 1, highest_level) Recursively call left_view(root->right, level + 1, highest_level) Step 4 -> Declare Function void left(struct node* root) Set int highest_level = 0 Call left_view(root, 1, &highest_level) Step 5-> In main() Call New passing value user want to insert as struct node* root = New(1) Call left(root) STOP
उदाहरण
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//create a structure of a node
struct node {
int data;
struct node *left, *right; //this pointer will point to the nodes attached with a node
};
struct node* New(int new_data) {
struct node* temp = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
//allocating memory to a pointer dynamically
temp->data = new_data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
void left_view(struct node* root, int level, int* highest_level) {
if (root == NULL) //if there is no node that means no data
return;
// this function will retrun the root node if there is only root node in a tree
if (*highest_level < level) {
printf("%d\t", root->data);
*highest_level = level;
}
// Recursive function
left_view(root->left, level + 1, highest_level);
left_view(root->right, level + 1, highest_level);
}
void left(struct node* root) {
int highest_level = 0;
left_view(root, 1, &highest_level);
}
int main() {
printf("left view of a binary tree is : ");
struct node* root = New(1);
root->left = New(0);
root->right = New(3);
root->right->left = New(2);
root->right->right = New(4);
left(root);
return 0;
} आउटपुट
यदि हम उपरोक्त प्रोग्राम चलाते हैं तो यह निम्न आउटपुट उत्पन्न करेगा।
left view of a binary tree is : 1 0 2