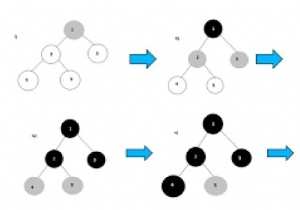
पिछली हफमैन कोड समस्या में, आवृत्ति को क्रमबद्ध नहीं किया गया था। यदि आवृत्ति सूची क्रमबद्ध क्रम में दी गई है, तो कोड निर्दिष्ट करने का कार्य अधिक कुशल हो रहा है।
इस समस्या में, हम दो खाली कतारों का उपयोग करेंगे। फिर प्रत्येक अद्वितीय वर्ण के लिए एक लीफ नोड बनाएं और इसे आवृत्ति के बढ़ते क्रम में कतार में डालें।
इस दृष्टिकोण में, एल्गोरिथ्म की जटिलता O(n) है।
इनपुट और आउटपुट
Input:
Different letters and their frequency in sorted order
Letters: {L, K, X, C, E, B, A, F}
Frequency: {1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 4}
Output:
Codes for the letters
L: 0000
K: 0001
X: 001
C: 010
E: 011
F: 10
B: 110
A: 111 एल्गोरिदम
हफमैन कोड (डेटा सूची, freqList, n)
इनपुट: डेटा सूची और आवृत्ति की सूची, और सूची में डेटा की संख्या n.
आउटपुट - कोड को दिए गए वर्ण।
Begin root := huffmanTree(dataList, freqList, n) //create root of Huffman tree create an array to store codes, and top pointer for that array. call getCodes(root, array, top) to find codes for each character. End
कोड प्राप्त करें (रूट:नोड, एरे, टॉप)
इनपुट: रूट नोड, कोड स्टोर करने के लिए ऐरे, ऐरे में सबसे ऊपर।
आउटपुट - प्रत्येक वर्ण के लिए कोड
Begin if leftChild(root) ≠φ then array[top] := 0 getCodes(leftChild(root), array, top) if rightChild(root) ≠φ then array[top] = 1 getCode(rightChild(root), array, top) if leftChild(root) = φ AND rightChild(root) = φ then display the character ch of root for all entries of the array do display the code in array[i] for character ch done End
हफ़मैन ट्री (डेटालिस्ट, फ़्रीकलिस्ट, एन)
इनपुट - डेटा सूची और आवृत्ति की सूची, और सूची में डेटा की संख्या n.
आउटपुट - हफ़मैन ट्री बनाता है
Begin for all different character ch do add node with ch and frequency of ch into queue q1 done while q1 is not empty OR size of q2 ≠ 1 do find two minimum node using q1 and q2 and add them as left and right child of a new node. add new node in q2 done delete node from q2 and return that node. End
उदाहरण
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
struct node {
char data;
int freq;
node *child0, *child1;
};
node *getNode(char d, int f) {
node *newNode = new node;
newNode->data = d;
newNode->freq = f;
newNode->child0 = NULL;
newNode->child1 = NULL;
return newNode;
}
node *findMinNode(queue<node*>&q1, queue<node*>&q2) {
node *minNode;
if(q1.empty()) { //if first queue is empty, delete and return node from second queue
minNode = q2.front();
q2.pop();
return minNode;
}
if(q2.empty()) { //if second queue is empty, delete and return node from first queue
minNode = q1.front();
q1.pop();
return minNode;
}
if((q1.front()->freq) < (q2.front()->freq)) { //find smaller from two queues
minNode = q1.front();
q1.pop();
return minNode;
}else {
minNode = q2.front();
q2.pop();
return minNode;
}
}
node *huffmanTree(char data[], int frequency[], int n) {
node *c0, *c1, *par;
node *newNode;
queue<node*> qu1, qu2;
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++) { //add all node to queue 1
newNode = getNode(data[i], frequency[i]);
qu1.push(newNode);
}
while(!(qu1.empty() && (qu2.size() == 1))) {
c0 = findMinNode(qu1, qu2); //find two minimum as two child
c1 = findMinNode(qu1, qu2);
node *newNode = getNode('#', c0->freq+c1->freq);
//intermediate node holds special character
par = newNode;
par->child0 = c0;
par->child1 = c1;
qu2.push(par); //add sub tree into queue 2
}
node *retNode = qu2.front();
qu2.pop();
return retNode;
}
void getCodes(node *rootNode, int array[], int n) { //array to store the code
if(rootNode->child0 != NULL) {
array[n] = 0;
getCodes(rootNode->child0, array, n+1);
}
if(rootNode->child1 != NULL) {
array[n] = 1;
getCodes(rootNode->child1, array, n+1);
}
if(rootNode->child0 == NULL && rootNode->child1 == NULL) { // when root is leaf node
cout << rootNode->data << ": ";
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++)
cout << array[i];
cout << endl;
}
}
void huffmanCodes(char data[], int frequency[], int n) {
node *rootNode = huffmanTree(data, frequency, n);
int array[50], top = 0;
getCodes(rootNode, array, top);
}
int main() {
char data[] = {'L', 'K', 'X', 'C', 'E', 'B', 'A', 'F'};
int frequency[] = {1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 4};
int n = sizeof(data)/sizeof(data[0]);
huffmanCodes(data, frequency, n);
} आउटपुट
L: 0000 K: 0001 X: 001 C: 010 E: 011 F: 10 B: 110 A: 111