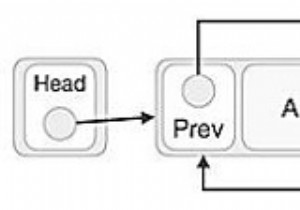
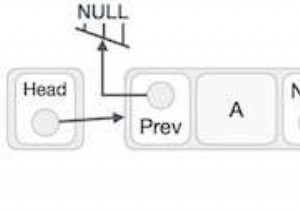
डेटा संरचना में लिंक सूची डेटा तत्वों का एक रैखिक संग्रह है। सूची के प्रत्येक तत्व या नोड में दो आइटम होते हैं - डेटा और अगले नोड का संदर्भ। अंतिम नोड में शून्य का संदर्भ है। एक लिंक्ड सूची में प्रवेश बिंदु को सूची का प्रमुख कहा जाता है।
सर्कुलर डबल लिंक्ड लिस्ट में दो लगातार तत्व पिछले और अगले पॉइंटर से जुड़े या जुड़े हुए हैं और अंतिम नोड अगले पॉइंटर द्वारा पहले नोड को इंगित करता है और पहला नोड पिछले पॉइंटर द्वारा अंतिम नोड को भी इंगित करता है।
एल्गोरिदम
Begin We shall create a class circulardoublylist which have the following functions: nod *create_node(int) = To memory allocated for node dynamically. insert_begin() = To Insert elements at beginning of the list. A) If the list is empty, then insert the node and set next and previous pointer as NULL. B) If the list is not empty, insert the data and set next and previous pointer and update them. insert_end() = To Insert elements at end of the list: A) If the list is empty create a node as circular doubly list. B) Find last node. C) Create node dynamically. D) Start going to be the next of new node. E) Make new node as previous node. F) Make last previous of new node. G) Make new node next of old last. insert_pos() = To insert elements at a specified position of the list: A) Insert the data. B) Enter the position at which element to be inserted. C) If the list is empty insert node at first. D) If list is not empty find node having position and next node. E) Insert the node between them. delete_pos() = To delete elements from specified position of the list: A) If list is empty, then return. B) Enter the position from which node needs to be deleted. C) If list has one node delete it and update next and prev pointers. D) If list has more than one nodes, then delete the node at particular position and update next and prev pointer. search() = To search element in the list: A) If the list is empty, then return. B) Enter the value to be searched. C) Print the position at which element to be found. D) If the element is not found, print not found. update() = To update value at a particular node: A) If the list is empty, then return. B) Enter the position of node to be updated. C) Enter the new value. D) Update the node. display() = To display the list. reverse() = To reverse the list. End
उदाहरण कोड
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
struct nod {
int info;
struct nod *n;
struct nod *p;
}*start, *last;
int count = 0;
class circulardoublylist {
public:
nod *create_node(int);
void insert_begin();
void insert_end();
void insert_pos();
void delete_pos();
void search();
void update();
void display();
void reverse();
circulardoublylist() {
start = NULL;
last = NULL;
}
};
int main() {
int c;
circulardoublylist cdl;
while (1) //perform switch operation {
cout<<"1.Insert at Beginning"<<endl;
cout<<"2.Insert at End"<<endl;
cout<<"3.Insert at Position"<<endl;
cout<<"4.Delete at Position"<<endl;
cout<<"5.Update Node"<<endl;
cout<<"6.Search Element"<<endl;
cout<<"7.Display List"<<endl;
cout<<"8.Reverse List"<<endl;
cout<<"9.Exit"<<endl;
cout<<"Enter your choice : ";
cin>>c;
switch(c) {
case 1:
cdl.insert_begin();
break;
case 2:
cdl.insert_end();
break;
case 3:
cdl.insert_pos();
break;
case 4:
cdl.delete_pos();
break;
case 5:
cdl.update();
break;
case 6:
cdl.search();
break;
case 7:
cdl.display();
break;
case 8:
cdl.reverse();
break;
case 9:
exit(1);
default:
cout<<"Wrong choice"<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
nod* circulardoublylist::create_node(int v) {
count++;
struct nod *t;
t = new(struct nod);
t->info = v;
t->n = NULL;
t->p = NULL;
return t;
}
void circulardoublylist::insert_begin() {
int v;
cout<<endl<<"Enter the element to be inserted: ";
cin>>v;
struct nod *t;
t = create_node(v);
if (start == last && start == NULL) {
cout<<"Element inserted in empty list"<<endl;
start = last = t;
start->n = last->n = NULL;
start->p = last->p = NULL;
} else {
t->n = start;
start->p = t;
start = t;
start->p = last;
last->n = start;
cout<<"Element inserted"<<endl;
}
}
void circulardoublylist::insert_end() {
int v;
cout<<endl<<"Enter the element to be inserted: ";
cin>>v;
struct nod *t;
t = create_node(v);
if (start == last && start == NULL) {
cout<<"Element inserted in empty list"<<endl;
start = last = t;
start->n= last->n = NULL;
start->p = last->p= NULL;
} else {
last->n= t;
t->p= last;
last = t;
start->p = last;
last->n= start;
}
}
void circulardoublylist::insert_pos() {
int v, pos, i;
cout<<endl<<"Enter the element to be inserted: ";
cin>>v;
cout<<endl<<"Enter the position of element inserted: ";
cin>>pos;
struct nod *t, *s, *ptr;
t = create_node(v);
if (start == last && start == NULL) {
if (pos == 1) {
start = last = t;
start->n = last->n = NULL;
start->p = last->p = NULL;
} else {
cout<<"Position out of range"<<endl;
count--;
return;
}
} else {
if (count < pos) {
cout<<"Position out of range"<<endl;
count--;
return;
}
s = start;
for (i = 1;i <= count;i++) {
ptr = s;
s = s->n;
if (i == pos - 1) {
ptr->n = t;
t->p= ptr;
t->n= s;
s->p = t;
cout<<"Element inserted"<<endl;
break;
}
}
}
}
void circulardoublylist::delete_pos() {
int pos, i;
nod *ptr, *s;
if (start == last && start == NULL) {
cout<<"List is empty, nothing to delete"<<endl;
return;
}
cout<<endl<<"Enter the position of element to be deleted: ";
cin>>pos;
if (count < pos) {
cout<<"Position out of range"<<endl;
return;
}
s = start;
if(pos == 1) {
count--;
last->n = s->n;
s->n->p = last;
start = s->n;
free(s);
cout<<"Element Deleted"<<endl;
return;
}
for (i = 0;i < pos - 1;i++ ) {
s = s->n;
ptr = s->p;
}
ptr->n = s->n;
s->n->p = ptr;
if (pos == count) {
last = ptr;
}
count--;
free(s);
cout<<"Element Deleted"<<endl;
}
void circulardoublylist::update() {
int v, i, pos;
if (start == last && start == NULL) {
cout<<"The List is empty, nothing to update"<<endl;
return;
}
cout<<endl<<"Enter the position of node to be updated: ";
cin>>pos;
cout<<"Enter the new value: ";
cin>>v;
struct nod *s;
if (count < pos) {
cout<<"Position out of range"<<endl;
return;
}
s = start;
if (pos == 1) {
s->info = v;
cout<<"Node Updated"<<endl;
return;
}
for (i=0;i < pos - 1;i++) {
s = s->n;
}
s->info = v;
cout<<"Node Updated"<<endl;
}
void circulardoublylist::search() {
int pos = 0, v, i;
bool flag = false;
struct nod *s;
if (start == last && start == NULL) {
cout<<"The List is empty, nothing to search"<<endl;
return;
}
cout<<endl<<"Enter the value to be searched: ";
cin>>v;
s = start;
for (i = 0;i < count;i++) {
pos++;
if (s->info == v) {
cout<<"Element "<<v<<" found at position: "<<pos<<endl;
flag = true;
}
s = s->n;
}
if (!flag)
cout<<"Element not found in the list"<<endl;
}
void circulardoublylist::display() {
int i;
struct nod *s;
if (start == last && start == NULL) {
cout<<"The List is empty, nothing to display"<<endl;
return;
}
s = start;
for (i = 0;i < count-1;i++) {
cout<<s->info<<"<->";
s = s->n;
}
cout<<s->info<<endl;
}
void circulardoublylist::reverse() {
if (start == last && start == NULL) {
cout<<"The List is empty, nothing to reverse"<<endl;
return;
}
struct nod *p1, *p2;
p1 = start;
p2 = p1->n;
p1->n = NULL;
p1->p= p2;
while (p2 != start) {
p2->p = p2->n;
p2->n = p1;
p1 = p2;
p2 = p2->p;
}
last = start;
start = p1;
cout<<"List Reversed"<<endl;
} आउटपुट
1.Insert at Beginning 2.Insert at End 3.Insert at Position 4.Delete at Position 5.Update Node 6.Search Element 7.Display List 8.Reverse List 9.Exit Enter your choice : 1 Enter the element to be inserted: 7 Element inserted in empty list 1.Insert at Beginning 2.Insert at End 3.Insert at Position 4.Delete at Position 5.Update Node 6.Search Element 7.Display List 8.Reverse List 9.Exit Enter your choice : 1 Enter the element to be inserted: 6 Element inserted 1.Insert at Beginning 2.Insert at End 3.Insert at Position 4.Delete at Position 5.Update Node 6.Search Element 7.Display List 8.Reverse List 9.Exit Enter your choice : 2 Enter the element to be inserted: 4 1.Insert at Beginning 2.Insert at End 3.Insert at Position 4.Delete at Position 5.Update Node 6.Search Element 7.Display List 8.Reverse List 9.Exit Enter your choice : 2 Enter the element to be inserted: 5 1.Insert at Beginning 2.Insert at End 3.Insert at Position 4.Delete at Position 5.Update Node 6.Search Element 7.Display List 8.Reverse List 9.Exit Enter your choice : 7 6<->7<->4<->5 1.Insert at Beginning 2.Insert at End 3.Insert at Position 4.Delete at Position 5.Update Node 6.Search Element 7.Display List 8.Reverse List 9.Exit Enter your choice : 6 Enter the value to be searched: 7 Element 7 found at position: 2 1.Insert at Beginning 2.Insert at End 3.Insert at Position 4.Delete at Position 5.Update Node 6.Search Element 7.Display List 8.Reverse List 9.Exit Enter your choice : 6 Enter the value to be searched: 2 Element not found in the list 1.Insert at Beginning 2.Insert at End 3.Insert at Position 4.Delete at Position 5.Update Node 6.Search Element 7.Display List 8.Reverse List 9.Exit Enter your choice : 4 Enter the position of element to be deleted: 4 Element Deleted 1.Insert at Beginning 2.Insert at End 3.Insert at Position 4.Delete at Position 5.Update Node 6.Search Element 7.Display List 8.Reverse List 9.Exit Enter your choice : 3 Enter the element to be inserted: 5 Enter the position of element inserted: 2 Element inserted 1.Insert at Beginning 2.Insert at End 3.Insert at Position 4.Delete at Position 5.Update Node 6.Search Element 7.Display List 8.Reverse List 9.Exit Enter your choice : 7 6<->5<->7<->4 1.Insert at Beginning 2.Insert at End 3.Insert at Position 4.Delete at Position 5.Update Node 6.Search Element 7.Display List 8.Reverse List 9.Exit Enter your choice : 8 List Reversed 1.Insert at Beginning 2.Insert at End 3.Insert at Position 4.Delete at Position 5.Update Node 6.Search Element 7.Display List 8.Reverse List 9.Exit Enter your choice : 7 4<->7<->5<->6 1.Insert at Beginning 2.Insert at End 3.Insert at Position 4.Delete at Position 5.Update Node 6.Search Element 7.Display List 8.Reverse List 9.Exit Enter your choice : 9