सर्कुलर लिंक्ड लिस्ट लिंक्ड लिस्ट का एक रूपांतर है जिसमें पहला तत्व अंतिम तत्व को इंगित करता है और अंतिम तत्व पहले तत्व को इंगित करता है। सिंगल लिंक्ड लिस्ट और डबल लिंक्ड लिस्ट दोनों को सर्कुलर लिंक्ड लिस्ट में बनाया जा सकता है।
डबल लिंक्ड लिस्ट में, अंतिम नोड का अगला पॉइंटर पहले नोड को इंगित करता है और पहले नोड का पिछला पॉइंटर दोनों दिशाओं में सर्कुलर बनाने वाले अंतिम नोड को इंगित करता है।
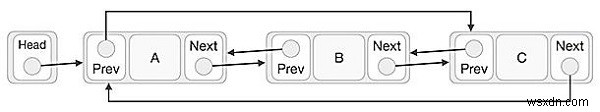
उपरोक्त दृष्टांत के अनुसार, निम्नलिखित महत्वपूर्ण बिंदु हैं जिन पर विचार किया जाना चाहिए।
-
अंतिम लिंक का अगला अंक डबल लिंक्ड सूची में सूची के पहले लिंक की ओर इशारा करता है।
-
पहली कड़ी के पिछले अंक दोगुनी लिंक की गई सूची के अंतिम की ओर इशारा करते हैं।
एल्गोरिदम
displayForward(): Begin ptr := head while ptr := null, do print ptr ->key, ptr ->data ptr := ptr -> next done End displayBackward(): Begin ptr := last while ptr := null, do print ptr ->key, ptr ->data ptr := ptr -> prev done End insertFirst(key, data): Begin create new node with key and data if list is empty, then last := node else head -> prev := node end if node -> next := head head := node End insertLast (key, data): Begin create new node with key and data if list is empty, then last := node else last -> next := node node -> prev:= last end if last := node End insertAfter(key, newKey, data): Begin current := head if head is null, then return false while key of current is not key, do if current -> next is not null, then return false else current := next of current end if done create new node with newKey and data if current = last, then next of node := null last := node else next of node := next of current prev of next of current := node end if prev of node := current next of current := node return true; End deleteFirst(): Begin tempNode := head if next of head is null, then last := null else prev of next of head := null end if head := next of head return tempNode End deleteLast(): Begin tempNode := last if next of head is null, then head := null else next of prev of last := null end if last := prev of last return tempNode End deleteNode(key): Begin curr := head and prev := null if head is null, then return null end if while key of currr is not same as key, do if next of curr is null, then return null else prev := curr curr := next of curr end if done if curr is head, then head := next of head, otherwise next of prev of curr = next of curr if curr is last, then last := prev of curr, otherwise prev of next of curr = prev of curr return curr End
उदाहरण
#include <iostream<
using namespace std;
class node {
public:
int data;
int key;
node *next;
node *prev;
};
//this link always point to first Link
node *head = NULL;
//this link always point to last Link
node *last = NULL;
node *current = NULL;
//is list empty
bool isEmpty() {
return head == NULL;
}
int length() {
int length = 0;
node *current;
for(current = head; current != NULL; current = current->next){
length++;
}
return length;
}
//display the list in from first to last
void displayForward() {
//start from the beginning
node *ptr = head;
//navigate till the end of the list
printf("\n[ ");
while(ptr != NULL) {
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
printf(" ]");
}
//display the list from last to first
void displayBackward() {
//start from the last
node *ptr = last;
//navigate till the start of the list
printf("\n[ ");
while(ptr != NULL) {
//print data
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
//move to next item
ptr = ptr ->prev;
}
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data) {
//create a link
node *link = new node();
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if(isEmpty()) {
//make it the last link
last = link;
}
else {
//update first prev link
head->prev = link;
}
//point it to old first link
link->next = head;
//point first to new first link
head = link;
}
//insert link at the last location
void insertLast(int key, int data) {
//create a link
node *link = new node();
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if(isEmpty()) {
//make it the last link
last = link;
}
else {
//make link a new last link
last->next = link;
//mark old last node as prev of new link
link->prev = last;
}
//point last to new last node
last = link;
}
//delete first item
node* deleteFirst() {
//save reference to first link
node *tempLink = head;
//if only one link
if(head->next == NULL){
last = NULL;
}
else {
head->next->prev = NULL;
}
head = head->next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
//delete link at the last location
node* deleteLast() {
//save reference to last link
node *tempLink = last;
//if only one link
if(head->next == NULL) {
head = NULL;
}
else {
last->prev->next = NULL;
}
last = last->prev;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
//delete a link with given key
node* del(int key) {
//start from the first link
node* current = head;
node* previous = NULL;
//if list is empty
if(head == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
//navigate through list
while(current->key != key) {
//if it is last node
if(current->next == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
else {
//store reference to current link
previous = current;
//move to next link
current = current->next;
}
}
//found a match, update the link
if(current == head) {
//change first to point to next link
head = head->next;
}
else {
//bypass the current link
current->prev->next = current->next;
}
if(current == last) {
//change last to point to prev link
last = current->prev;
}
else {
current->next->prev = current->prev;
}
return current;
}
bool insertAfter(int key, int newKey, int data) {
//start from the first link
node *current = head;
//if list is empty
if(head == NULL) {
return false;
}
//navigate through list
while(current->key != key) {
//if it is last node
if(current->next == NULL) {
return false;
}
else {
//move to next link
current = current->next;
}
}
//create a link
node *newLink = new node();
newLink->key = newKey;
newLink->data = data;
if(current == last) {
newLink->next = NULL;
last = newLink;
}
else {
newLink->next = current->next;
current->next->prev = newLink;
}
newLink->prev = current;
current->next = newLink;
return true;
}
main() {
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertFirst(5,40);
insertFirst(6,56);
printf("\nList (First to Last): ");
displayForward();
printf("\n");
printf("\nList (Last to first): ");
displayBackward();
printf("\nList , after deleting first record: ");
deleteFirst();
displayForward();
printf("\nList , after deleting last record: ");
deleteLast();
displayForward();
printf("\nList , insert after key(4) : ");
insertAfter(4,7, 13);
displayForward();
printf("\nList , after delete key(4) : ");
del(4);
displayForward();
} आउटपुट
List (First to Last): [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) (1,10) ] List (Last to first): [ (1,10) (2,20) (3,30) (4,1) (5,40) (6,56) List , after deleting first record: [ (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) (1,10) ] List , after deleting last record: [ (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) ] List , insert after key(4) : [ (5,40) (4,1) (7,13) (3,30) (2,20) ] List , after delete key(4) : [ (5,40) (7,13) (3,30) (2,20) ]