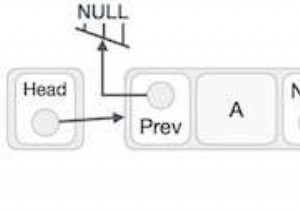
डेटा संरचना में लिंक सूची डेटा तत्वों का एक रैखिक संग्रह है। सूची के प्रत्येक तत्व या नोड में दो आइटम होते हैं - डेटा और अगले नोड का संदर्भ। अंतिम नोड में शून्य का संदर्भ है। लिंक की गई सूची में प्रवेश बिंदु को सूची का प्रमुख कहा जाता है।
एक डबल लिंक्ड सूची में अनुक्रमिक रूप से जुड़े रिकॉर्ड्स का एक सेट होता है जिसे नोड्स कहा जाता है। प्रत्येक नोड में तीन फ़ील्ड होते हैं:एक डेटा फ़ील्ड और दो लिंक फ़ील्ड; नोड्स फ़ील्ड के अनुक्रम में पिछले और अगले नोड के संदर्भ।
डबल लिंक की गई सूची को क्रमबद्ध करने के मामले में, सॉर्ट किए गए डेटा फ़ील्ड मानों के मानों के अनुसार लिंक की गई सूची क्रमबद्ध रहेगी।
एल्गोरिदम
Begin function createnode() to insert node in the list: it creates a newnode and inserts the number in the data field of the newnode. It checks whether the list is empty or not. If the list is empty put the node as first element and update head. Both prev and next pointers will be initialized with NULL. If list is not empty, then this newnode will be inserted into the existing linked list in such a way that ultimately the linked list will remain sorted. Prev and next pointers will be updated accordingly. End Begin function display_head() to display the list from the head: Initialize c=0. Initialize pointer variable with the head node address while (c <= i ) Print the node info Update pointer variable Increment c. End Begin function dispslay_tail() to display the list from the tail: Initialize m=0. Initialize pointer variable with the tail node address while (m <= i ) Print the node info Update pointer variable Increment m. End
उदाहरण कोड
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct nod {
int d;
nod *n, *p;
}
*p = NULL, *head = NULL, *r = NULL, *np = NULL, *tail = NULL;
int c = 0;
void createnode(int n) {
np = new nod;
np->d = n;
np->n = NULL;
np->p = NULL;
if (c == 0) {
tail = np;
head = np;
p = head;
p->n = head;
p->p = head;
c++;
} else if (c == 1) {
p = head;
r = p;
if (np->d < p->d) {
np->n = p;
p->p = np;
head = np;
p->n = np;
np->p = p;
tail = p;
} else if (np->d > p->d) {
p->n = np;
np->p = p;
np->n= head;
p->p = np;
}
c++;
} else {
p = head;
r = p;
if (np->d < p->d) {
np->n = p;
p->p = np;
head = np;
do {
p = p->n;
}
while (p->n != r);
tail = p;
p->n = np;
np->p = p;
} else if (np->d > p->d) {
while (p->n != head && np->d > p->d) {
r = p;
p = p->n;
if (p->n == head && (p->d < np->d)) {
p->n = np;
np->p = p;
np->n = head;
tail = np;
head->p = np;
break;
} else if (np->d< p->d) {
r->n= np;
np->p = r;
np->n= p;
p->p= np;
if (p->n != head) {
do {
p = p->n;
}
while (p->n != head);
}
tail = p;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
void display_head(int i) {
nod *t = head;
int c = 0;
while (c <= i) {
cout<<t->d<<"\t";
t = t->n;
c++;
}
cout<<endl;
}
void display_tail(int i) {
nod *t = tail;
int m = 0;
while (m <= i) {
cout<<t->d<<"\t";
t = t->p;
m++;
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main() {
int i = 0, n, a, ch;
cout<<"enter the no of nodes\n";
cin>>n;
while (i < n) {
cout<<"\nenter value of node\n";
cin>>a;
createnode(a);
i++;
}
cout<<"\nsorting Doubly Linked List head first\n";
display_head(n);
cout<<"\nsorting Doubly Linked List tail first\n";
display_tail(n);
} आउटपुट
enter the no of nodes 5 enter value of node 7 enter value of node 4 enter value of node 6 enter value of node 2 enter value of node 1 sorting Doubly Linked List head first 1 2 4 6 7 1 sorting Doubly Linked List tail first 7 6 4 2 1 7