बाइनरी ट्री को देखते हुए प्रोग्राम को दिए गए कई रास्तों में से रूट से लीफ तक के सबसे छोटे रास्ते का पता लगाना चाहिए।
चूँकि हम पेड़ को बाएँ से दाएँ पार करते हैं, इसलिए यदि जड़ से पत्ती तक कई छोटे रास्ते हैं, तो प्रोग्राम पेड़ के बाईं ओर सबसे छोटा रास्ता सबसे पहले ट्रैवर्स करेगा।
हम एक कतार का उपयोग कर सकते हैं जो लेवल ऑर्डर ट्रैवर्सल का उपयोग करके प्रत्येक स्तर को पार करेगी और कम से कम स्तरों वाले पथ को प्रिंट किया जाएगा क्योंकि यह रूट से लीफ तक का सबसे छोटा रास्ता होगा
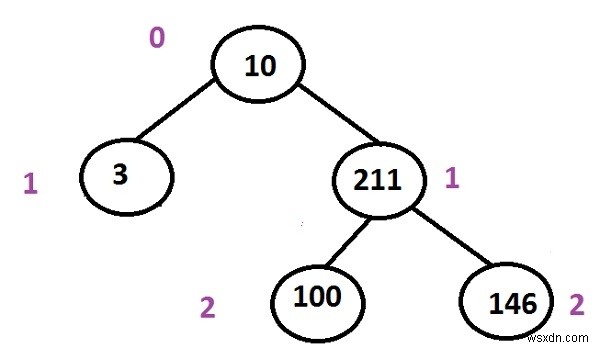
ऊपर के पेड़ में, जड़ से पत्ती तक के कई रास्ते हैं
10 -> 3 (this one is the shortest path amongst all) 10 -> 211 -> 100 10 -> 211 -> 146
उदाहरण
Input : 10 3 211 100 146 Output : 10 3
एल्गोरिदम
Step 1 -> create a structure of a node as struct node struct node *left, *right int data End Step 2 -> function to create a node node* newnode(int data) node *temp = new node temp->data = data temp->left = temp->right= NULL return temp Step 3 -> create function for calculating path void path(int data, unordered_map <int,int> prnt) IF prnt[data] = data Return End path(prnt[data], prnt) print prnt[data] step 4 -> function for finding out the left path void left(Node* root) create STL queue<Node*> que que.push(root) int leaf = -1 Node* temp = NULL Create STL unordered_map<int, int> prnt prnt[root->data] = root->data Loop While !que.empty() temp = que.front() que.pop() IF !temp->left && !temp->right leaf = temp->data break End Else IF temp->left que.push(temp->left) prnt[temp->left->data] = temp->data End IF temp->right que.push(temp->right) prnt[temp->right->data] = temp->data End End End path(leaf, prnt) print leaf Step 5 -> In main() Create tree using Node* root = newnode(90) root->left = newnode(21) call left(root) stop
उदाहरण
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// structure of a node
struct Node {
struct Node *left,*right;
int data;
};
//function to create a new node
Node* newnode(int data){
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = NULL;
temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
//function to set a path
void path(int data, unordered_map <int,int> prnt) {
if (prnt[data] == data)
return;
path(prnt[data], prnt);
cout << prnt[data] << " ";
}
//function for a leaf path
void left(Node* root) {
queue<Node*> que;
que.push(root);
int leaf = -1;
Node* temp = NULL;
unordered_map<int, int> prnt;
prnt[root->data] = root->data;
while (!que.empty()){
temp = que.front();
que.pop();
if (!temp->left && !temp->right{
leaf = temp->data;
break;
} else {
if (temp->left){
que.push(temp->left);
prnt[temp->left->data] = temp->data;
}
if (temp->right){
que.push(temp->right);
prnt[temp->right->data] = temp->data;
}
}
}
path(leaf, prnt);
cout << leaf << " ";
}
int main(){
Node* root = newnode(90);
root->left = newnode(21);
root->right = newnode(32);
root->left->left = newnode(45);
root->right->left = newnode(52);
root->right->right = newnode(27);
root->left->left->left = newnode(109);
root->left->left->right = newnode(101);
root->right->right->left = newnode(78);
left(root);
return 0;
} आउटपुट
यदि हम उपरोक्त प्रोग्राम चलाते हैं तो यह निम्न आउटपुट उत्पन्न करेगा
90 32 52