अवधारणा
किसी दिए गए अप्रत्यक्ष ग्राफ के संबंध में, सत्यापित करें कि क्या इसमें l आकार का एक स्वतंत्र सेट है। यदि आकार का एक स्वतंत्र सेट मौजूद है तो 'हां' प्रिंट करें, अन्यथा 'नहीं' प्रिंट करें। यह ध्यान दिया जाना चाहिए कि ग्राफ में एक स्वतंत्र सेट को शिखर के एक सेट के रूप में परिभाषित किया जाता है जो सीधे एक दूसरे से जुड़े नहीं होते हैं।
इनपुट
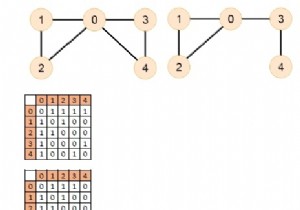
L = 4, graph = [[1, 0, 1, 0, 0], [0, 1, 1, 0, 0],[1, 1, 1, 1, 1], [0, 0, 1, 1, 0],[0, 0, 1, 0, 1]];
आउटपुट
Yes
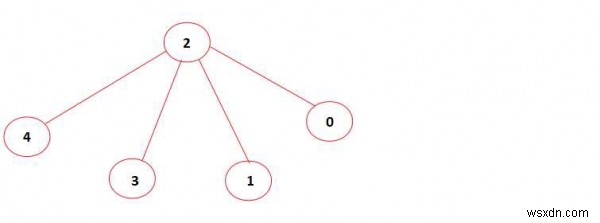
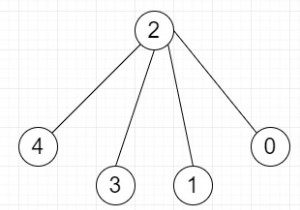
उपरोक्त ग्राफ में आकार 4 का एक स्वतंत्र सेट है (शीर्ष 0, 1, 3, 4 एक दूसरे से सीधे जुड़े नहीं हैं)। इसलिए आउटपुट 'हां' है।
इनपुट
L = 4, graph =[[1, 1, 1, 0, 0],[1, 1, 1, 0, 0],[1, 1, 1, 1, 1],[0, 0, 1, 1, 0],[0, 0, 1, 0, 1]];
आउटपुट
No
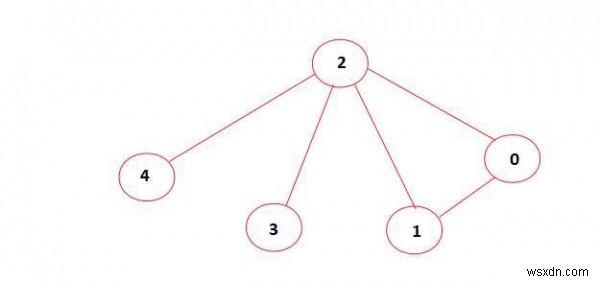
आरेख में, उपरोक्त ग्राफ़ में आकार 4 का एक स्वतंत्र सेट नहीं है। इसलिए आउटपुट 'नहीं' है।
विधि
- सबसे पहले, एक वैरिएबल सोल को बूलियन फाल्स वैल्यू के साथ इनिशियलाइज़ करें।
- दिए गए ग्राफ से L आकार के शीर्षों के सभी संभावित सेट निर्धारित करें।
- यह देखा गया है कि यदि आकार l का एक स्वतंत्र सेट मिलता है, तो सोल के मान को ट्रू में बदलें और वापस लौटें।
- अन्यथा अन्य संभावित सेटों की जांच जारी रखें।
- अंत में, यदि सोल सत्य है, तो 'हां' प्रिंट करें अन्यथा 'नहीं' प्रिंट करें।
उदाहरण
// C++ code to check if a given graph
// contains an independent set of size k
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Shows function prototype
bool check1(int[][5], vector<int>&, int);
// Shows function to construct a set of given size l
bool func(int graph1[][5], vector<int>&arr1,
int l, int index1, bool sol1[]){
// Verify if the selected set is independent or not.
// Used to change the value of sol to True and return
// if it is independent
if (l == 0){
if (check1(graph1, arr1, arr1.size())){
sol1[0] = true;
return true;
}
}
else{
// Now set of size l can be formed even if we don't
// include the vertex at current index.
if (index1 >= l){
vector<int> newvec(arr1.begin(), arr1.end());
newvec.push_back(index1);
return (func(graph1, newvec, l - 1,
index1 - 1, sol1) or
func(graph1, arr1, l, index1 - 1, sol1));
}
// Now set of size l cannot be formed if we don't
// include the vertex at current index.
else{
arr1.push_back(index1);
return func(graph1, arr1, l - 1,
index1 - 1, sol1);
}
}
}
// Shows function to verify if the given set is
// independent or not
// arr --> set of size l (contains the
// index of included vertex)
bool check1(int graph1[][5], vector<int>&arr1, int n1){
// Verify if each vertex is connected to any other
// vertex in the set or not
for (int i = 0; i < n1; i++)
for (int j = i + 1; j < n1; j++)
if (graph1[arr1[i]][arr1[j]] == 1)
return false;
return true;
}
// Driver Code
int main(){
int graph1[][5] = {{1, 0, 1, 0, 0},{0, 1, 1, 0, 0},{1, 1, 1, 1, 1},{0, 0, 1, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 0, 1}};
int l = 4;
vector<int> arr1; // Empty set
bool sol1[] = {false};
int n1 = sizeof(graph1) /
sizeof(graph1[0]);
func(graph1, arr1, l, n1 - 1, sol1);
if (sol1[0])
cout << "Yes" << endl;
else
cout << "No" << endl;
return 0;
} आउटपुट
Yes