यह उदाहरण दर्शाता है कि Android में JSON को कैसे पार्स किया जाए।
चरण 1 - एंड्रॉइड स्टूडियो में एक नया प्रोजेक्ट बनाएं, फाइल ⇒ न्यू प्रोजेक्ट पर जाएं और एक नया प्रोजेक्ट बनाने के लिए सभी आवश्यक विवरण भरें।
चरण 2 - निम्न कोड को res/layout/activity_main.xml में जोड़ें।
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <TextView android:id="@+id/tvName" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:layout_marginTop="50dp" android:text="Name" android:textColor="#000" android:textSize="20sp" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/tvSalary" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:layout_marginTop="80dp" android:text="Salary" android:textColor="#000" android:textSize="20sp" /> </RelativeLayout>
चरण 3 - निम्न कोड को src/MainActivity.java
में जोड़ेंpackage com.example.myapplication;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
import org.json.JSONException;
import org.json.JSONObject;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
String JSON_STRING="{\"employee\":{\"name\":\"adolf hitler\",\"salary\":65000}}";
String name, salary;
TextView employeeName, employeeSalary;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
// get the reference of TextView's
employeeName=(TextView) findViewById(R.id.tvName);
employeeSalary=(TextView) findViewById(R.id.tvSalary);
try {
// get JSONObject from JSON file
JSONObject obj=new JSONObject(JSON_STRING);
// fetch JSONObject named employee
JSONObject employee=obj.getJSONObject("employee");
// get employee name and salary
name=employee.getString("name");
salary=employee.getString("salary");
// set employee name and salary in TextView's
employeeName.setText("Name: "+name);
employeeSalary.setText("Salary: "+salary);
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} चरण 4 - मेनिफ़ेस्ट/AndroidManifest.xml
में निम्न कोड जोड़ें<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.myapplication"> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round" android:supportsRtl="true" android:theme="@style/AppTheme"> <activity android:name=".MainActivity"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>
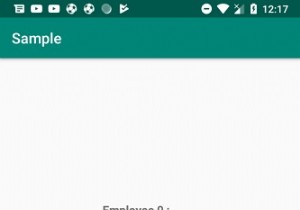
आइए आपके एप्लिकेशन को चलाने का प्रयास करते हैं। मुझे लगता है कि आपने अपने वास्तविक Android मोबाइल डिवाइस को अपने कंप्यूटर से कनेक्ट कर लिया है। एंड्रॉइड स्टूडियो से ऐप चलाने के लिए, अपने प्रोजेक्ट की गतिविधि फ़ाइल में से एक खोलें और टूलबार से रन आइकन पर क्लिक करें। एक विकल्प के रूप में अपने मोबाइल डिवाइस का चयन करें और फिर अपने मोबाइल डिवाइस की जांच करें जो आपकी डिफ़ॉल्ट स्क्रीन प्रदर्शित करेगा -