डेटा संरचना संरचित तरीके से व्यवस्थित डेटा का संग्रह है। इसे नीचे बताए अनुसार दो प्रकारों में बांटा गया है -
-
रैखिक डेटा संरचना - डेटा को एक रेखीय तरीके से व्यवस्थित किया जाता है। उदाहरण के लिए, सरणियाँ, संरचनाएँ, ढेर, कतारें, लिंक्ड सूचियाँ।
-
गैर-रेखीय डेटा संरचना - डेटा को एक श्रेणीबद्ध तरीके से व्यवस्थित किया जाता है। उदाहरण के लिए, पेड़, ग्राफ, सेट, टेबल।
कतार
यह एक रेखीय डेटा संरचना है, जहां सम्मिलन पीछे के छोर पर किया जाता है और विलोपन सामने के छोर पर किया जाता है।
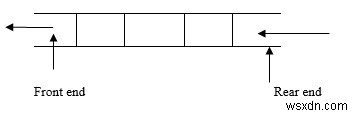
कतार का क्रम है फीफो - फर्स्ट इन फर्स्ट आउट
ऑपरेशन
- सम्मिलित करें - एक कतार में एक तत्व सम्मिलित करना।
- हटाएं - कतार से किसी तत्व को हटाना।
शर्तें
-
क्यू ओवर फ्लो - एक एलिमेंट को पूरी क्यू में डालने की कोशिश कर रहा है।
-
प्रवाह के तहत कतार - एक खाली कतार से एक तत्व को हटाने की कोशिश कर रहा है।
एल्गोरिदम
सम्मिलन ( ) . के लिए एक एल्गोरिथम नीचे दिया गया है -
- कतार ओवरफ्लो की जांच करें।
if (r==n)
printf ("Queue overflow") - अन्यथा, कतार में एक तत्व डालें।
q[r] = item r++
कार्यक्रम
क्यू में तत्वों को सम्मिलित करने के लिए सी प्रोग्राम निम्नलिखित है -
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX 50
void insert();
int array[MAX];
int rear = - 1;
int front = - 1;
main(){
int add_item;
int choice;
while (1){
printf("1.Insert element to queue \n");
printf("2.Display elements of queue \n");
printf("3.Quit \n");
printf("Enter your choice : ");
scanf("%d", &choice);
switch (choice){
case 1:
insert();
break;
case 2:
display();
break;
case 3:
exit(1);
default:
printf("Wrong choice \n");
}
}
}
void insert(){
int add_item;
if (rear == MAX - 1)
printf("Queue Overflow \n");
else{
if (front == - 1)
/*If queue is initially empty */
front = 0;
printf("Inset the element in queue : ");
scanf("%d", &add_item);
rear = rear + 1;
array[rear] = add_item;
}
}
void display(){
int i;
if (front == - 1)
printf("Queue is empty \n");
else{
printf("Queue is : \n");
for (i = front; i <= rear; i++)
printf("%d ", array[i]);
printf("\n");
}
} आउटपुट
जब उपरोक्त प्रोग्राम को निष्पादित किया जाता है, तो यह निम्नलिखित परिणाम उत्पन्न करता है -
1.Insert element to queue 2.Display elements of queue 3.Quit Enter your choice: 1 Inset the element in queue: 34 1.Insert element to queue 2.Display elements of queue 3.Quit Enter your choice: 1 Inset the element in queue: 24 1.Insert element to queue 2.Display elements of queue 3.Quit Enter your choice: 2 Queue is: 34 24 1.Insert element to queue 2.Display elements of queue 3.Quit Enter your choice: 3