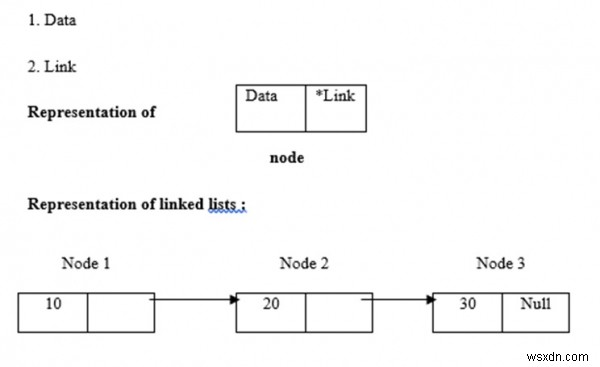
लिंक्ड सूचियाँ गतिशील मेमोरी आवंटन का उपयोग करती हैं अर्थात वे उसी के अनुसार बढ़ती और सिकुड़ती हैं। उन्हें नोड्स के संग्रह के रूप में परिभाषित किया गया है। यहां, नोड्स के दो भाग होते हैं, जो डेटा और लिंक हैं। डेटा, लिंक और लिंक्ड सूचियों का प्रतिनिधित्व नीचे दिया गया है -
लिंक की गई सूचियों पर संचालन
C भाषा में लिंक्ड सूचियों पर तीन प्रकार के ऑपरेशन होते हैं, जो इस प्रकार हैं -
- सम्मिलन
- हटाना
- ट्रैवर्सिंग
हटाना
नीचे दिए गए एक उदाहरण पर विचार करें -
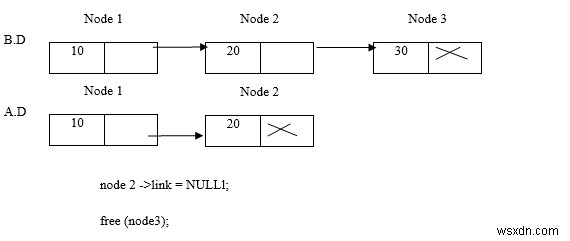
नोड 2 हटाएं
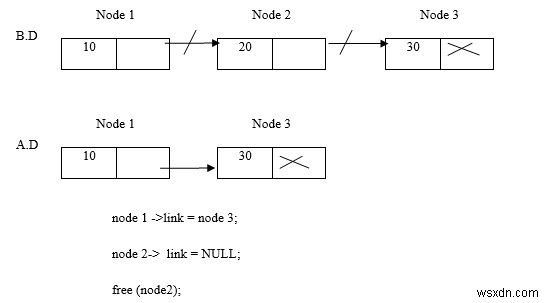
नोड 1 हटाएं
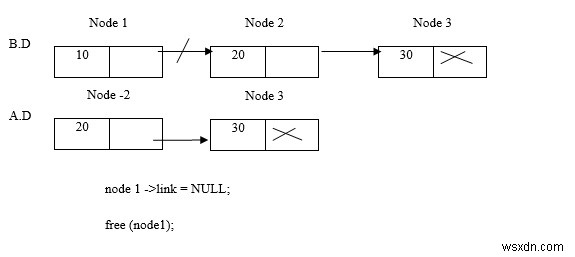
नोड 3 हटाएं
कार्यक्रम
लिंक्ड सूचियों में तत्वों को हटाने के लिए सी कार्यक्रम निम्नलिखित है -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Node{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data){
struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
void deleteNode(struct Node **head_ref, int position){
//if list is empty
if (*head_ref == NULL)
return;
struct Node* temp = *head_ref;
if (position == 0){
*head_ref = temp->next;
free(temp);
return;
}
for (int i=0; temp!=NULL && i<position-1; i++)
temp = temp->next;
if (temp == NULL || temp->next == NULL)
return;
struct Node *next = temp->next->next;
free(temp->next); // Free memory
temp->next = next;
}
void printList(struct Node *node){
while (node != NULL){
printf(" %d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
}
int main(){
struct Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 7);
push(&head, 1);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 8);
puts("Created List: ");
printList(head);
deleteNode(&head, 3);
puts("\n List after Deletion at position 3: ");
printList(head);
return 0;
} आउटपुट
जब उपरोक्त प्रोग्राम को निष्पादित किया जाता है, तो यह निम्नलिखित परिणाम उत्पन्न करता है -
Created List: 8 2 3 1 7 List after Deletion at position 3: 8 2 3 7