मेमोरी को गतिशील रूप से आवंटित करके स्टैक ओवर फ़्लो और स्टैक अंडर फ़्लो से बचा जा सकता है।
सी प्रोग्रामिंग भाषा में स्टैक के तहत किए गए संचालन इस प्रकार हैं -
- पुश
- पॉप
पुश
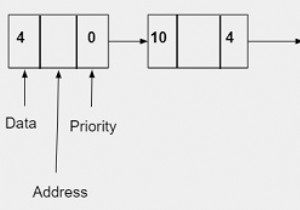
लिंक्ड सूची का मूल कार्यान्वयन निम्नलिखित है -
&item = 10 newnode = (node*) malloc (sizeof (node)); newnode ->data = item; newnode ->link = NULL; newnode ->link = start; start = newnode;
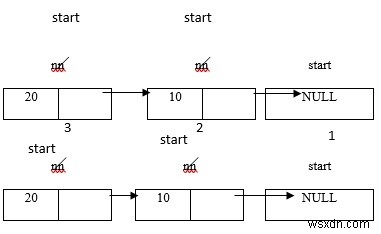
पॉप
वाक्य रचना इस प्रकार है -
वाक्यविन्यास
if (start = = NULL)
printf("Deletion is not possible.List is empty")
else{
temp = start;
start = start link;
free (temp);
} कार्यक्रम
लिंक्ड सूचियों का उपयोग करके स्टैक के लिए सी प्रोग्राम निम्नलिखित है -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node{
int info;
struct node *ptr;
}*top,*top1,*temp;
int topelement();
void push(int data);
void pop();
void empty();
void display();
void destroy();
void stack_count();
void create();
int count = 0;
void main(){
int no, ch, e;
printf("\n 1 - Push");
printf("\n 2 - Pop");
printf("\n 3 - Top");
printf("\n 4 - Empty");
printf("\n 5 - Exit");
printf("\n 6 - Display");
printf("\n 7 - Stack Count");
printf("\n 8 - Destroy stack");
create();
while (1){
printf("\n Enter choice : ");
scanf("%d", &ch);
switch (ch){
case 1:
printf("Enter element : ");
scanf("%d", &no);
push(no);
break;
case 2:
pop();
break;
case 3:
if (top == NULL)
printf("stack is empty");
else{
e = topelement();
printf("\n Top element : %d", e);
}
break;
case 4:
empty();
break;
case 5:
exit(0);
case 6:
display();
break;
case 7:
stack_count();
break;
case 8:
destroy();
break;
default :
printf(" wrong choice:Try again ");
break;
}
}
}
//empty stack
void create(){
top = NULL;
}
void stack_count(){
printf("\n no: of elements in stack : %d", count);
}
//push data
void push(int data){
if (top == NULL){
top =(struct node *)malloc(1*sizeof(struct node));
top->ptr = NULL;
top->info = data;
}
else{
temp =(struct node *)malloc(1*sizeof(struct node));
temp->ptr = top;
temp->info = data;
top = temp;
}
count++;
}
void display(){
top1 = top;
if (top1 == NULL){
printf("empty stack");
return;
}
while (top1 != NULL){
printf("%d ", top1->info);
top1 = top1->ptr;
}
}
void pop(){
top1 = top;
if (top1 == NULL){
printf("\n error");
return;
}
else
top1 = top1->ptr;
printf("\n Popped value : %d", top->info);
free(top);
top = top1;
count--;
}
int topelement(){
return(top->info);
}
//check stack empty or not
void empty(){
if (top == NULL)
printf("\n empty stack");
else
printf("\n stack not empty with %d values", count);
}
void destroy(){
top1 = top;
while (top1 != NULL){
top1 = top->ptr;
free(top);
top = top1;
top1 = top1->ptr;
}
free(top1);
top = NULL;
printf("\n all are destroyed");
count = 0;
} आउटपुट
जब उपरोक्त प्रोग्राम को निष्पादित किया जाता है, तो यह निम्नलिखित परिणाम उत्पन्न करता है -
1 - Push 2 - Pop 3 - Top 4 - Empty 5 - Exit 6 - Display 7 - Stack Count 8 - Destroy stack Enter choice: 1 Enter element: 23 Enter choice: 1 Enter element: 45 Enter choice: 1 Enter element: 56 Enter choice: 2 Popped value: 56 Enter choice: 6 45 23 Enter choice: 8 all are destroyed Enter choice: 6 empty stack Enter choice: 5