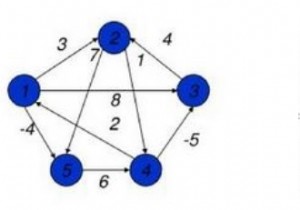
सिंगल सोर्स शॉर्टेस्ट पाथ एल्गोरिथम (गैर-नकारात्मक वजन के लिए) को दिज्क्स्ट्रा एल्गोरिथम भी कहा जाता है। इसके आसन्न मैट्रिक्स प्रतिनिधित्व के साथ एक दिया गया ग्राफ G(V,E) है, और एक स्रोत शीर्ष भी प्रदान किया गया है। ग्राफ़ जी के किसी अन्य शीर्ष से स्रोत शीर्ष के बीच न्यूनतम सबसे छोटा पथ खोजने के लिए डिजस्ट्रा का एल्गोरिदम।
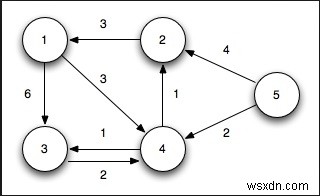
नोड को प्रारंभ करने से किसी अन्य नोड तक, सबसे छोटी दूरी ज्ञात करें। इस समस्या में ग्राफ को आसन्न मैट्रिक्स का उपयोग करके दर्शाया जाता है। (लागत मैट्रिक्स और आसन्नता मैट्रिक्स इस उद्देश्य के लिए समान हैं)।
इनपुट - आसन्न मैट्रिक्स -
0 3 6 ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞ 3 0 2 1 ∞ ∞ ∞ 6 2 0 1 4 2 ∞ ∞ 1 1 0 2 ∞ 4 ∞ ∞ 4 2 0 2 1 ∞ ∞ 2 ∞ 2 0 1 ∞ ∞ ∞ 4 1 1 0
आउटपुट -
0 to 1, Using: 0, Cost: 3 0 to 2, Using: 1, Cost: 5 0 to 3, Using: 1, Cost: 4 0 to 4, Using: 3, Cost: 6 0 to 5, Using: 2, Cost: 7 0 to 6, Using: 4, Cost: 7
एल्गोरिदम
dijkstraShortestPath(n, dist, next, start)
इनपुट - नोड्स की कुल संख्या n, प्रत्येक शीर्ष के लिए दूरी सूची, स्टोर करने के लिए अगली सूची जो नोड आगे आता है, और बीज या प्रारंभ शीर्ष।
आउटपुट − प्रारंभ से अन्य सभी शीर्षों तक का सबसे छोटा पथ।
Begin create a status list to hold the current status of the selected node for all vertices u in V do status[u] := unconsidered dist[u] := distance from source using cost matrix next[u] := start done status[start] := considered, dist[start] := 0 and next[start] := φ while take unconsidered vertex u as distance is minimum do status[u] := considered for all vertex v in V do if status[v] = unconsidered then if dist[v] > dist[u] + cost[u,v] then dist[v] := dist[u] + cost[u,v] next[v] := u done done End
उदाहरण(C++)
#include<iostream>
#define V 7
#define INF 999
using namespace std;
//Cost matrix of the graph
int costMat[V][V] = {
{0, 3, 6, INF, INF, INF, INF},
{3, 0, 2, 1, INF, INF, INF},
{6, 2, 0, 1, 4, 2, INF},
{INF, 1, 1, 0, 2, INF, 4},
{INF, INF, 4, 2, 0, 2, 1},
{INF, INF, 2, INF, 2, 0, 1},
{INF, INF, INF, 4, 1, 1, 0}
};
int minimum(int *status, int *dis, int n){
int i, min, index;
min = INF;
for(i = 0; i<n; i++)
if(dis[i] < min && status[i] == 1){
min = dis[i];
index = i;
}
if(status[index] == 1)
return index;//minimum unconsidered vertex distance
else
return -1;//when all vertices considered
}
void dijkstra(int n, int *dist,int *next, int s){
int status[V];
int u, v;
//initialization
for(u = 0; u<n; u++){
status[u] = 1;//unconsidered vertex
dist[u] = costMat[u][s];//distance from source
next[u] = s;
}
//for source vertex
status[s] = 2; dist[s] = 0; next[s] = -1;//-1 for starting vertex
while((u = minimum(status, dist, n)) > -1){
status[u] = 2;//now considered
for(v = 0; v<n; v++)
if(status[v] == 1)
if(dist[v] > dist[u] + costMat[u][v]){
dist[v] = dist[u] + costMat[u][v];//update distance
next[v] = u;
}
}
}
main(){
int dis[V], next[V], i, start = 0;
dijkstra(V, dis, next, start);
for(i = 0; i<V; i++)
if(i != start)
cout << start << " to " << i <<", Using: " << next[i] << ", Cost: " << dis[i] << endl;
} आउटपुट
0 to 1, Using: 0, Cost: 3 0 to 2, Using: 1, Cost: 5 0 to 3, Using: 1, Cost: 4 0 to 4, Using: 3, Cost: 6 0 to 5, Using: 2, Cost: 7 0 to 6, Using: 4, Cost: 7