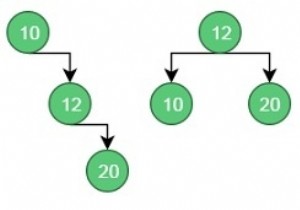
पूर्णांकों का एक सेट क्रमबद्ध क्रम में दिया गया है और एक अन्य सरणी freq आवृत्ति गणना के लिए दिया गया है। हमारा काम सभी खोजों के लिए न्यूनतम लागत खोजने के लिए उन डेटा के साथ एक बाइनरी सर्च ट्री बनाना है।
उप-समस्याओं के समाधान को हल करने और संग्रहीत करने के लिए एक सहायक सरणी लागत [एन, एन] बनाई गई है। समस्या को हल करने के लिए कॉस्ट मैट्रिक्स डेटा को बॉटम-अप तरीके से होल्ड करेगा।
इनपुट और आउटपुट
Input:
The key values as node and the frequency.
Keys = {10, 12, 20}
Frequency = {34, 8, 50}
Output:
The minimum cost is 142.
These are possible BST from the given values.
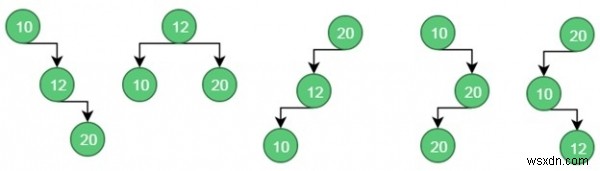 For case 1, the cost is: (34*1) + (8*2) + (50*3) = 200
For case 2, the cost is: (8*1) + (34*2) + (50*2) = 176.
Similarly for case 5, the cost is: (50*1) + (34 * 2) + (8 * 3) = 142 (Minimum)
For case 1, the cost is: (34*1) + (8*2) + (50*3) = 200
For case 2, the cost is: (8*1) + (34*2) + (50*2) = 176.
Similarly for case 5, the cost is: (50*1) + (34 * 2) + (8 * 3) = 142 (Minimum) एल्गोरिदम
optCostBst(keys, freq, n)
इनपुट: BST में डालने के लिए कुंजियाँ, प्रत्येक कुंजी के लिए आवृत्ति, कुंजियों की संख्या।
आउटपुट: इष्टतम बीएसटी बनाने के लिए न्यूनतम लागत।
Begin define cost matrix of size n x n for i in range 0 to n-1, do cost[i, i] := freq[i] done for length in range 2 to n, do for i in range 0 to (n-length+1), do j := i + length – 1 cost[i, j] := ∞ for r in range i to j, done if r > i, then c := cost[i, r-1] else c := 0 if r < j, then c := c + cost[r+1, j] c := c + sum of frequency from i to j if c < cost[i, j], then cost[i, j] := c done done done return cost[0, n-1] End
उदाहरण
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int sum(int freq[], int low, int high) { //sum of frequency from low to high range
int sum = 0;
for (int k = low; k <=high; k++)
sum += freq[k];
return sum;
}
int minCostBST(int keys[], int freq[], int n) {
int cost[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) //when only one key, move along diagonal elements
cost[i][i] = freq[i];
for (int length=2; length<=n; length++) {
for (int i=0; i<=n-length+1; i++) { //from 0th row to n-length+1 row as i
int j = i+length-1;
cost[i][j] = INT_MAX; //initially store to infinity
for (int r=i; r<=j; r++) {
//find cost when r is root of subtree
int c = ((r > i)?cost[i][r-1]:0)+((r < j)?cost[r+1][j]:0)+sum(freq, i, j);
if (c < cost[i][j])
cost[i][j] = c;
}
}
}
return cost[0][n-1];
}
int main() {
int keys[] = {10, 12, 20};
int freq[] = {34, 8, 50};
int n = 3;
cout << "Cost of Optimal BST is: "<< minCostBST(keys, freq, n);
} आउटपुट
Cost of Optimal BST is: 142