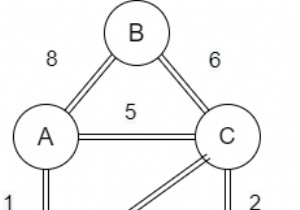
बेलमैन-फोर्ड एल्गोरिथम का उपयोग स्रोत शीर्ष से किसी अन्य शीर्ष तक न्यूनतम दूरी ज्ञात करने के लिए किया जाता है। डिजस्ट्रा के एल्गोरिथ्म के साथ इस एल्गोरिथम के बीच मुख्य अंतर यह है कि डिजस्ट्रा के एल्गोरिथ्म में हम नकारात्मक वजन को संभाल नहीं सकते हैं, लेकिन यहां हम इसे आसानी से संभाल सकते हैं।
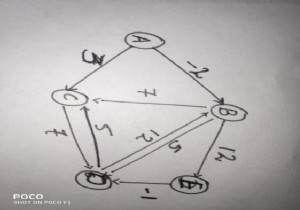
बेलमैन-फोर्ड एल्गोरिथम दूरी को बॉटम-अप तरीके से ढूंढता है। सबसे पहले, यह उन दूरियों को ढूंढता है जिनके रास्ते में केवल एक किनारा होता है। उसके बाद सभी संभावित समाधान खोजने के लिए पथ की लंबाई बढ़ाएं।
इनपुट और आउटपुट
Input: The cost matrix of the graph: 0 6 ∞ 7 ∞ ∞ 0 5 8 -4 ∞ -2 0 ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞ -3 0 9 2 ∞ 7 ∞ 0 Output: Source Vertex: 2 Vert: 0 1 2 3 4 Dist: -4 -2 0 3 -6 Pred: 4 2 -1 0 1 The graph has no negative edge cycle
एल्गोरिदम
bellmanFord(dist, pred, source)
इनपुट - दूरी सूची, पूर्ववर्ती सूची और स्रोत शीर्ष।
आउटपुट - सच है, जब एक नकारात्मक चक्र पाया जाता है।
Begin iCount := 1 maxEdge := n * (n - 1) / 2 //n is number of vertices for all vertices v of the graph, do dist[v] := ∞ pred[v] := ϕ done dist[source] := 0 eCount := number of edges present in the graph create edge list named edgeList while iCount < n, do for i := 0 to eCount, do if dist[edgeList[i].v] > dist[edgeList[i].u] + (cost[u,v] for edge i) dist[edgeList[i].v] > dist[edgeList[i].u] + (cost[u,v] for edge i) pred[edgeList[i].v] := edgeList[i].u done done iCount := iCount + 1 for all vertices i in the graph, do if dist[edgeList[i].v] > dist[edgeList[i].u] + (cost[u,v] for edge i), then return true done return false End
उदाहरण
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#define V 5
#define INF 999
using namespace std;
//Cost matrix of the graph (directed) vertex 5
int costMat[V][V] = {
{0, 6, INF, 7, INF},
{INF, 0, 5, 8, -4},
{INF, -2, 0, INF, INF},
{INF, INF, -3, 0, 9},
{2, INF, 7, INF, 0}
};
typedef struct {
int u, v, cost;
}edge;
int isDiagraph() {
//check the graph is directed graph or not
int i, j;
for(i = 0; i<V; i++) {
for(j = 0; j<V; j++) {
if(costMat[i][j] != costMat[j][i]) {
return 1; //graph is directed
}
}
}
return 0;//graph is undirected
}
int makeEdgeList(edge *eList) {
//create edgelist from the edges of graph
int count = -1;
if(isDiagraph()) {
for(int i = 0; i<V; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j<V; j++) {
if(costMat[i][j] != 0 && costMat[i][j] != INF) {
count++; //edge find when graph is directed
eList[count].u = i; eList[count].v = j;
eList[count].cost = costMat[i][j];
}
}
}
}else {
for(int i = 0; i<V; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j<i; j++) {
if(costMat[i][j] != INF) {
count++; //edge find when graph is undirected
eList[count].u = i; eList[count].v = j;
eList[count].cost = costMat[i][j];
}
}
}
}
return count+1;
}
int bellmanFord(int *dist, int *pred,int src) {
int icount = 1, ecount, max = V*(V-1)/2;
edge edgeList[max];
for(int i = 0; i<V; i++) {
dist[i] = INF; //initialize with infinity
pred[i] = -1; //no predecessor found.
}
dist[src] = 0;//for starting vertex, distance is 0
ecount = makeEdgeList(edgeList); //edgeList formation
while(icount < V) { //number of iteration is (Vertex - 1)
for(int i = 0; i<ecount; i++) {
if(dist[edgeList[i].v] > dist[edgeList[i].u] + costMat[edgeList[i].u][edgeList[i].v]) { //relax edge and set predecessor
dist[edgeList[i].v] = dist[edgeList[i].u] + costMat[edgeList[i].u][edgeList[i].v];
pred[edgeList[i].v] = edgeList[i].u;
}
}
icount++;
}
//test for negative cycle
for(int i = 0; i<ecount; i++) {
if(dist[edgeList[i].v] > dist[edgeList[i].u] + costMat[edgeList[i].u][edgeList[i].v]) {
return 1; //indicates the graph has negative cycle
}
}
return 0; //no negative cycle
}
void display(int *dist, int *pred) {
cout << "Vert: ";
for(int i = 0; i<V; i++)
cout <<setw(3) << i << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << "Dist: ";
for(int i = 0; i<V; i++)
cout << setw(3) << dist[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << "Pred: ";
for(int i = 0; i<V; i++)
cout << setw(3) << pred[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
int dist[V], pred[V], source, report;
source = 2;
report = bellmanFord(dist, pred, source);
cout << "Source Vertex: " << source<<endl;
display(dist, pred);
if(report)
cout << "The graph has a negative edge cycle" << endl;
else
cout << "The graph has no negative edge cycle" << endl;
} आउटपुट
Source Vertex: 2 Vert: 0 1 2 3 4 Dist: -4 -2 0 3 -6 Pred: 4 2 -1 0 1 The graph has no negative edge cycle