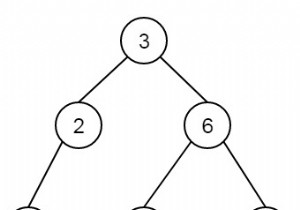
द्विआधारी खोज एक खोज एल्गोरिथ्म है जो एक क्रमबद्ध सरणी के भीतर लक्ष्य मान की स्थिति का पता लगाता है। बाइनरी खोज लक्ष्य मान की तुलना सॉर्ट किए गए सरणी के मध्य तत्व से करती है। द्विआधारी खोज की समय जटिलता ओ (1) है। यह एक C++ प्रोग्राम है जिसमें हम विभिन्न क्रियान्वित करते हैं। C++ STL में बाइनरी सर्च फंक्शन्स
एल्गोरिदम
Begin Initialize the vector of integer values. The functions are used here: binary_search(start_pointer, end_pointer, value) = Returns true if the value present in array otherwise false. lower_bound(start_pointer, end_pointer, value) = Returns pointer to “position of value” if container contains 1 occurrence of value. Returns pointer to “first position of value” if container contains multiple occurrence of value. Returns pointer to “position of next higher number than value” if container does not contain occurrence of value. upper_bound(start_pointer, end_pointer, value) = Returns pointer to “position of next higher valuethan value” if container contains 1 occurrence of value. Returns pointer to “first position of next higher number than last occurrence of value” if container contains multiple occurrence of value. Returns pointer to “position of next higher number than value” if container does not contain occurrence of value. Print the results. End.
उदाहरण कोड
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> a = {6,7,10,14,16,20};
if (binary_search(a.begin(), a.end(), 50))
cout << "50 exists in vector";
else
cout << "50 does not exist";
cout << endl;
if (binary_search(a.begin(), a.end(), 7))
cout << "7 exists in the vector";
else
cout << "7 does not exist";
cout << endl;
cout << "The position of 7 using lower_bound ";
cout << lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), 7) - a.begin();
cout << endl;
cout << "The position of 7 using upper_bound ";
cout << upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), 7) - a.begin();
cout << endl;
} आउटपुट
50 does not exist 7 exists in the vector The position of 7 using lower_bound 1 The position of 7 using upper_bound 2