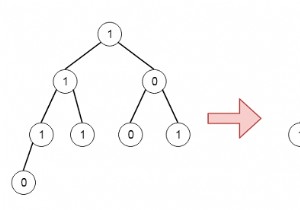
मान लीजिए कि हमारे पास एक बाइनरी ट्री है। जैसा कि हम जानते हैं कि बाइनरी ट्री का संक्षिप्त एन्कोडिंग न्यूनतम संभव स्थान के करीब प्रदर्शन करता है। n'th कातालान संख्या n विभिन्न नोड्स के साथ संरचनात्मक रूप से भिन्न बाइनरी ट्री की संख्या द्वारा निर्दिष्ट है। यदि n बड़ा है, तो यह लगभग 4n है; इस प्रकार, हमें इसे एन्कोड करने के लिए कम से कम log2(4) n =2n बिट्स की आवश्यकता होती है। इसलिए एक संक्षिप्त बाइनरी ट्री 2n + O(n) बिट्स का उपभोग करेगा।
तो, अगर इनपुट पसंद है
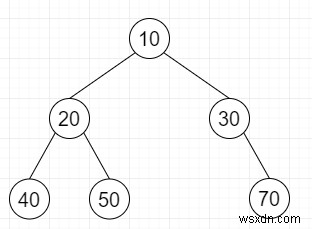
तो आउटपुट होगा
एन्कोडेड -
संरचना सूची 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0
डेटा सूची 10 20 40 50 30 70
डिकोड किया गया - ऊपर दिखाया गया पेड़।
इसे हल करने के लिए, हम इन चरणों का पालन करेंगे -
- एक फ़ंक्शन को परिभाषित करें Encode(), यह रूट लेगा, struc नाम की एक सूची, डेटा नाम की एक सूची,
- यदि रूट NULL के समान है, तो −
- struc के अंत में 0 डालें
- वापसी
- struc के अंत में 1 डालें
- डेटा के अंत में रूट का मान डालें
- एनकोड (रूट, संरचना, डेटा के बाईं ओर)
- एनकोड (रूट का अधिकार, संरचना, डेटा)
- एक फ़ंक्शन डिकोड () को परिभाषित करें, यह struc नाम की एक सूची, डेटा नाम की एक सूची लेगा,
- यदि संरचना का आकार <=0, तो −
- पूर्ण वापसी
- vb :=संरचना का पहला तत्व
- struc से सामने का तत्व हटाएं
- यदि b 1 के समान है, तो −
- कुंजी:=डेटा का पहला तत्व
- डेटा से फ्रंट एलिमेंट हटाएं
- रूट =कुंजी के साथ नया नोड
- रूट के बाईं ओर :=डिकोड (struc, डेटा)
- रूट का अधिकार :=डिकोड (struc, डेटा)
- रिटर्न रूट
- पूर्ण वापसी
उदाहरण (C++)
आइए बेहतर समझ पाने के लिए निम्नलिखित कार्यान्वयन देखें -
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class TreeNode {
public:
int val;
TreeNode *left, *right;
TreeNode(int data) {
val = data;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
};
void Encode(TreeNode *root, list<bool>&struc, list<int>&data){
if(root == NULL){
struc.push_back(0);
return;
}
struc.push_back(1);
data.push_back(root->val);
Encode(root->left, struc, data);
Encode(root->right, struc, data);
}
TreeNode *Decode(list<bool>&struc, list<int>&data){
if(struc.size() <= 0)
return NULL;
bool b = struc.front();
struc.pop_front();
if(b == 1){
int key = data.front();
data.pop_front();
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(key);
root->left = Decode(struc, data);
root->right = Decode(struc, data);
return root;
}
return NULL;
}
void preorder_trav(TreeNode* root){
if(root){
cout << "key: "<< root->val;
if(root->left)
cout << " | left child: "<< root->left->val;
if(root->right)
cout << " | right child: "<< root->right->val;
cout << endl;
preorder_trav(root->left);
preorder_trav(root->right);
}
}
main() {
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(10);
root->left = new TreeNode(20);
root->right = new TreeNode(30);
root->left->left = new TreeNode(40);
root->left->right = new TreeNode(50);
root->right->right = new TreeNode(70);
cout << "The Tree\n";
preorder_trav(root);
list<bool> struc;
list<int> data;
Encode(root, struc, data);
cout << "\nEncoded Tree\n";
cout << "Structure List\n";
list<bool>::iterator si; // Structure iterator
for(si = struc.begin(); si != struc.end(); ++si)
cout << *si << " ";
cout << "\nData List\n";
list<int>::iterator di; // Data iIterator
for(di = data.begin(); di != data.end(); ++di)
cout << *di << " ";
TreeNode *newroot = Decode(struc, data);
cout << "\n\nPreorder traversal of decoded tree\n";
preorder_trav(newroot);
} इनपुट
root->left = new TreeNode(20); root->right = new TreeNode(30); root->left->left = new TreeNode(40); root->left->right = new TreeNode(50); root->right->right = new TreeNode(70);
आउटपुट
The Tree key: 10 | left child: 20 | right child: 30 key: 20 | left child: 40 | right child: 50 key: 40 key: 50 key: 30 | right child: 70 key: 70 Encoded Tree Structure List 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 Data List 10 20 40 50 30 70 Preorder traversal of decoded tree key: 10 | left child: 20 | right child: 30 key: 20 | left child: 40 | right child: 50 key: 40 key: 50 key: 30 | right child: 70 key: 70