अवधारणा
किसी दिए गए बाइनरी ट्री के संबंध में, इसके लिए निम्न मान लौटाएं।
-
प्रत्येक स्तर के संबंध में, यदि इस स्तर पर पत्तियाँ हैं तो सभी पत्तों का योग ज्ञात कीजिए। अन्यथा इसे अनदेखा करें।
-
सभी राशियों के गुणन की गणना करें और उसे वापस करें।
इनपुट
Root of following tree 3 / \ 8 6 \ 10
आउटपुट
80
पहले स्तर में पत्ते नहीं होते हैं। दूसरे स्तर में एक पत्ता 8 होता है और तीसरे स्तर में भी एक पत्ता 10 होता है। तो परिणाम 8*10 =80
. होता हैइनपुट
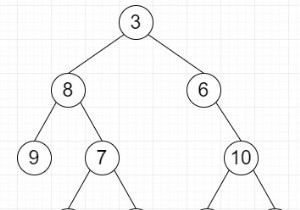
Root of following tree 3 / \ 8 6 / \ \ 9 7 10 / \ / \ 2 12 5 11
आउटपुट
270
पहले दो स्तरों में पत्ते नहीं होते हैं। थर्डलेवल में सिंगल लीफ 9 है। अंतिम लेवल में 2, 12, 5 और 11 के चार पत्ते हैं। तो परिणाम 9 * (2 + 12 + 5 + 11) =270
है।विधि
एक सरल समाधान के संबंध में, हम ऊपर से नीचे तक सभी स्तरों के लिए लीफ योग की पुनरावर्ती गणना करते हैं। उसके बाद उन स्तरों के योगों को गुणा करें जिनमें पत्तियाँ हैं। यहाँ, इस समाधान की समय जटिलता O(n^2) होगी।
फिर से एक कुशल समाधान के संबंध में, हम कतार आधारित स्तर के आदेश ट्रैवर्सल को लागू करते हैं। यहां, ट्रैवर्सल करते समय, हम सभी अलग-अलग स्तरों को अलग-अलग संसाधित करते हैं। प्रत्येक संसाधित स्तर के संबंध में, सत्यापित करें कि इसमें पत्तियां हैं या नहीं। इस मामले में, यदि इसने लीफ नोड्स के योग की गणना की है। अंत में, सभी राशियों का उत्पाद लौटाएं।
उदाहरण
/* Iterative C++ program to find sum of data of all leaves
of a binary tree on same level and then multiply sums
obtained of all levels. */
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Shows a Binary Tree Node
struct Node1 {
int data1;
struct Node1 *left1, *right1;
};
// Shows helper function to check if a Node is leaf of tree
bool isLeaf(Node1* root1){
return (!root1->left1 && !root1->right1);
}
/* Compute sum of all leaf Nodes at each level and returns
multiplication of sums */
int sumAndMultiplyLevelData(Node1* root1){
// Here tree is empty
if (!root1)
return 0;
int mul1 = 1; /* Used To store result */
// Build an empty queue for level order tarversal
queue<Node1*> q1;
// Used to Enqueue Root and initialize height
q1.push(root1);
// Perform level order traversal of tree
while (1) {
// NodeCount1 (queue size) indicates number of Nodes
// at current lelvel.
int NodeCount1 = q1.size();
// Now if there are no Nodes at current level, we are done
if (NodeCount1 == 0)
break;
// Used to initialize leaf sum for current level
int levelSum1 = 0;
// Shows a boolean variable to indicate if found a leaf
// Node at current level or not
bool leafFound1 = false;
// Used to Dequeue all Nodes of current level and Enqueue
all
// Nodes of next level
while (NodeCount1 > 0) {
// Process next Node of current level
Node1* Node1 = q1.front();
/* Now if Node is a leaf, update sum at the level */
if (isLeaf(Node1)) {
leafFound1 = true;
levelSum1 += Node1->data1;
}
q1.pop();
// Add children of Node
if (Node1->left1 != NULL)
q1.push(Node1->left1);
if (Node1->right1 != NULL)
q1.push(Node1->right1);
NodeCount1--;
}
// Now if we found at least one leaf, we multiply
// result with level sum.
if (leafFound1)
mul1 *= levelSum1;
}
return mul1; // Here, return result
}
//Shows utility function to create a new tree Node
Node1* newNode(int data1){
Node1* temp1 = new Node1;
temp1->data1 = data1;
temp1->left1 = temp1->right1 = NULL;
return temp1;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main(){
Node1* root1 = newNode(3);
root1->left1 = newNode(8);
root1->right1 = newNode(6);
root1->left1->right1 = newNode(7);
root1->left1->left1 = newNode(9);
root1->left1->right1->left1 = newNode(2);
root1->left1->right1->right1 = newNode(12);
root1->right1->right1 = newNode(10);
root1->right1->right1->left1 = newNode(5);
root1->right1->right1->right1 = newNode(11);
cout << "Final product value = "
<< sumAndMultiplyLevelData(root1) <<endl;
return 0;
} आउटपुट
Final product value = 270