इस लेख में, हम नीचे दिए गए समस्या कथन के समाधान के बारे में जानेंगे।
समस्या कथन - हमें पॉज़ फॉर्म दिया गया है, हमें इसे इसके समकक्ष एसओपी फॉर्म में बदलने की जरूरत है
रूपांतरण पहले पॉज़ फॉर्म में अक्षरों की संख्या की गणना करके और फिर सभी अधिकतम और न्यूनतम अवधि की गणना करके किया जा सकता है।
आइए अब नीचे दिए गए कार्यान्वयन में अवधारणा को देखें-
उदाहरण
# Python code to convert standard POS form
# to standard SOP form
# to calculate number of variables
def count_no_alphabets(POS):
i = 0
no_var = 0
# total no. of alphabets before will be equal to alphabets before first '.' character
while (POS[i]!='.'):
# character is a alphabet or not
if (POS[i].isalpha()):
no_var+= 1
i+= 1
return no_var
# maximum terms in an integer
def Cal_Max_terms(Max_terms, POS):
a = ""
i = 0
while (i<len(POS)):
if (POS[i]=='.'):
# binary to decimal conversion
b = int(a, 2)
# append each min term(integer type) into the list
Max_terms.append(b)
# assign empty strings
a =""
i+= 1
elif(POS[i].isalpha()):
# checking whether variable is having complement as superscript
if(i + 1 != len(POS) and POS[i + 1]=="'"):
# concatenating the string with '1'
a += '1'
# incrementing by 2 because 1 for alphabet and another for a symbol "'"
i += 2
else:
# concatenating the string with '0'
a += '0'
i += 1
else:
i+= 1
# append last min term(integer type) into the list
Max_terms.append(int(a, 2))
# conversion of minterms in binary and finally converting it to SOP
def Cal_Min_terms(Max_terms, no_var, start_alphabet):
# declaration of the list
Min_terms =[]
# calculation of total no. of terms formed by all variables max = 2**no_var
for i in range(0, max):
# is current term present in max_terms or not
if (Max_terms.count(i)== 0):
# converting integer to binary
b = bin(i)[2:]
# loop used for inserting 0's before the
# binary value so that its length will be
# equal to no. of variables present in
# each product term
while(len(b)!= no_var):
b ='0'+b
# appending the max terms(integer) in the list
Min_terms.append(b)
SOP = ""
# iterated untill minterms are available
for i in Min_terms:
# fetching the variable
value = start_alphabet
# iterate till there are 0's and 1's
for j in i:
# check whether the varailble is complemented or not
if (j =='0'):
# concatenating vaue and complement operator
SOP = SOP + value+ "'"
# check the non complement variable
else:
# concatenating value
SOP = SOP + value
# increment the alphabet by the next adjacent alaphabet
value = chr(ord(value)+1)
# concatenating the "+" operator
SOP = SOP+ "+"
# for discarding the extra '+'
SOP = SOP[:-1]
return SOP
# main function
def main():
# input
POS_expr ="(A'+B'+C).(A+B+C').(A+B'+C).(A'+B+C)"
Max_terms = []
no_var = count_no_alphabets(POS_expr)
Cal_Max_terms(Max_terms, POS_expr)
SOP_expr = Cal_Min_terms(Max_terms, no_var, POS_expr[1])
print("Standard SOP form of " + POS_expr + " ==> " + SOP_expr)
# Driver code
if __name__=="__main__":
main() आउटपुट
Standard SOP form of (A'+B'+C).(A+B+C').(A+B'+C).(A'+B+C) ==> A'B'C'+A'BC+AB'C+ABC
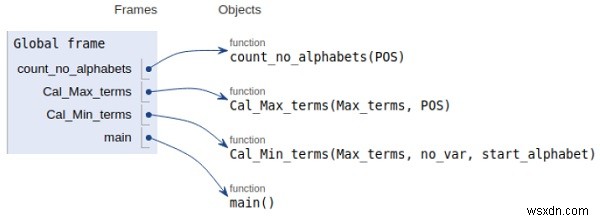
सभी चर स्थानीय दायरे में घोषित किए गए हैं और उनके संदर्भ ऊपर दिए गए चित्र में देखे गए हैं।
निष्कर्ष
इस लेख में, हमने सीखा है कि कैसे हम पॉस को सोप फॉर्म में बदल सकते हैं