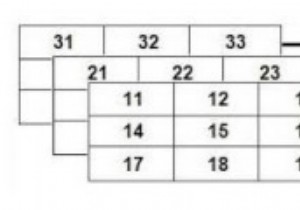
एक 4 आयामी सरणी 3Darrays की एक सरणी है।
एल्गोरिदम
Begin. Declare the variables. Declare the array elements. Take the no of elements as input. Take the elements as input. Print the elements stored in array. End.
यहाँ 4D सरणी का एक उदाहरण दिया गया है।
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a[2][2][3][2];
cout << "Enter the elements of array: \n";
for(int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < 2; ++j) {
for(int k = 0; k < 3; ++k ) {
for(int l = 0; l < 2; ++l ) {
cin >> a[i][j][k][l];
}
}
}
}
cout<<"\narray elements are stored as:"<<endl;
for(int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < 2; ++j) {
for(int k = 0; k < 3; ++k) {
for(int l = 0; l < 2; ++l) {
cout << "a[" << i << "][" << j << "][" << k << "] [" <<l<<"]= " << a[i][j][k][l] << endl;
}
}
}
}
return 0;
} आउटपुट
Enter the elements of array: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 array elements are stored as: a[0][0][0] [0]= 1 a[0][0][0] [1]= 2 a[0][0][1] [0]= 3 a[0][0][1] [1]= 4 a[0][0][2] [0]= 5 a[0][0][2] [1]= 6 a[0][1][0] [0]= 7 a[0][1][0] [1]= 8 a[0][1][1] [0]= 9 a[0][1][1] [1]= 10 a[0][1][2] [0]= 11 a[0][1][2] [1]= 12 a[1][0][0] [0]= 13 a[1][0][0] [1]= 14 a[1][0][1] [0]= 15 a[1][0][1] [1]= 16 a[1][0][2] [0]= 17 a[1][0][2] [1]= 18 a[1][1][0] [0]= 19 a[1][1][0] [1]= 20 a[1][1][1] [0]= 21 a[1][1][1] [1]= 22 a[1][1][2] [0]= 23 a[1][1][2] [1]= 24