कार्य अतिरिक्त स्थान का उपयोग किए बिना लिंक की गई सूची के अंत से शुरू होने वाले नोड्स को प्रिंट करना है, जिसका अर्थ है कि कोई अतिरिक्त चर नहीं होना चाहिए, इसके बजाय पहले नोड को इंगित करने वाले हेड पॉइंटर को स्थानांतरित कर दिया जाएगा।
उदाहरण
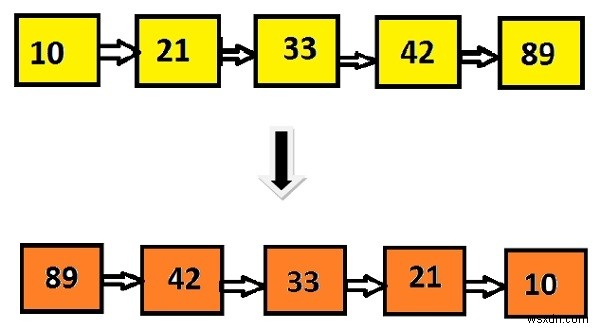
Input: 10 21 33 42 89 Output: 89 42 33 21 10
लिंक की गई सूची को उल्टे क्रम में प्रिंट करने के लिए कई समाधान हो सकते हैं, जैसे पुनरावर्ती दृष्टिकोण (अतिरिक्त स्थान का उपयोग करें), लिंक की गई सूची को उलट दें (दिए गए लिंक की गई सूची में संशोधन की आवश्यकता है), तत्वों को एक स्टैक पर धकेलना और फिर पॉप और तत्वों को प्रदर्शित करना एक-एक करके (स्थान O(n) की आवश्यकता है), लेकिन ये समाधान O(1) की तुलना में अधिक स्थान का उपयोग करते प्रतीत होते हैं।
O(1) से अधिक का उपयोग किए बिना परिणाम प्राप्त करने के लिए हम - . कर सकते हैं
- लिंक की गई सूची में नोड्स की संख्या की गणना करें
- i =n से 1 तक लूप करें और i-वें स्थान के नोड को प्रिंट करें।
एल्गोरिदम
START Step 1 -> create node variable of type structure Declare int data Declare pointer of type node using *next Step 2 ->Declare function int get(struct node* head) Declare variable as int count=0 Declare struct node *newme=head Loop While newme!=NULL Increment count by 1 Set newme = newme->next End Return count Step 3 -> Declare Function void push(node** headref, char newdata) Allocate memory using malloc Set newnode->data = newdata Set newnode->next = (*headref) Set (*headref) = newnode Step 4 -> Declare function int getN(struct node* head, int n) Declare struct node* cur = head Loop for int i=0 and i<n-1 && cur != NULL and i++ Set cur=cur->next End Return cur->dataStep 5 -> Declare function void reverse(node *head) Declare int n = get(head) Loop For int i=n and i>=1 and i— Print getN(head,i) End Step 6 ->In Main() Create list using node* head = NULL Insert elements through push(&head, 89) Call reverse(head) STOP
उदाहरण
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
//node structure
struct node {
int data;
struct node* next;
};
void push(struct node** headref, int newdata) {
struct node* newnode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newnode->data = newdata;
newnode->next = (*headref);
(*headref) = newnode;
}
int get(struct node* head) {
int count = 0;
struct node* newme = head;
while (newme != NULL){
count++;
newme = newme->next;
}
return count;
}
int getN(struct node* head, int n) {
struct node* cur = head;
for (int i=0; i<n-1 && cur != NULL; i++)
cur = cur->next;
return cur->data;
}
void reverse(node *head) {
int n = get(head);
for (int i=n; i>=1; i--)
printf("%d ", getN(head, i));
}
int main() {
struct node* head = NULL; //create a first node
push(&head, 89); //pushing element in the list
push(&head, 42);
push(&head, 33);
push(&head, 21);
push(&head, 10);
reverse(head); //calling reverse function
return 0;
} आउटपुट
यदि हम उपरोक्त प्रोग्राम चलाते हैं तो यह निम्न आउटपुट उत्पन्न करेगा
89 42 33 21 10