हमें दिए गए इंडेक्स पर लिंक्ड लिस्ट के नोड्स के डेटा को प्रिंट करना होता है। ऐरे लिंक्ड लिस्ट के विपरीत आम तौर पर इंडेक्स नहीं होता है इसलिए हमें पूरी लिंक्ड लिस्ट को पार करना होता है और किसी विशेष पर पहुंचने पर डेटा को प्रिंट करना होता है।
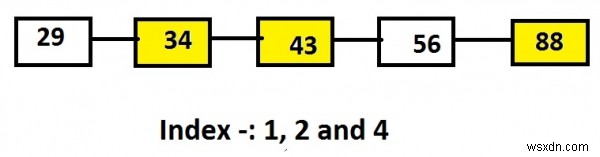
मान लीजिए, सूची में नोड्स 29, 34, 43, 56 और 88 हैं और इंडेक्स का मान 1, 2 और 4 है, जो इन इंडेक्स पर नोड्स होंगे जो कि 34, 43 और 88 हैं।
उदाहरण
Linked list: 29->34->43->56->88 Input: 1 2 4 Output: 34 43 88
लिंक्ड लिस्ट के उपरोक्त प्रतिनिधित्व में पीले हाइलाइट किए गए नोड्स मुद्रित किए जाने वाले नोड या किसी विशेष इंडेक्स पर स्थित नोड्स होते हैं।
यहां इस्तेमाल किए गए दृष्टिकोण में एक पॉइंटर और एक काउंटर वेरिएबल को 1 से शुरू करना शामिल है जो कि जब भी नोड को पार किया जाता है तो वृद्धि होगी। काउंटर का मिलान कुंजी मान से किया जाता है। जब कुंजी काउंटर मान के साथ मेल खाती है, तो नोड संरचना की ओर इशारा करने वाला पॉइंटर नोड के डेटा को प्रिंट करेगा और अगले नोड में वृद्धि करेगा और इसी तरह हमें विशेष कुंजी पर नोड्स देगा।
नीचे दिया गया कोड दिए गए एल्गोरिथम के c कार्यान्वयन को दर्शाता है।
एल्गोरिदम
START Step 1 -> create node variable of type structure Declare int data Declare pointer of type node using *next Step 2 -> create struct node* intoList(int data) Create newnode using malloc Set newnode->data = data newnode->next = NULL return newnode step 3 -> Declare function void displayList(struct node *catchead) create struct node *temp IF catchead = NULL Print list is empty return End Set temp = catchead Loop While (temp != NULL) print temp->data set temp = temp->next End Step 4 -> Declare Function int search(int key,struct node *head) Set int index Create struct node *newnode Set index = 0 and newnode = head Loop While (newnode != NULL & newnode->data != key) Set index++ Set newnode = newnode->next End return (newnode != NULL) ? index : -1 step 5 -> In Main() create node using struct node* head = intoList(9) call displayList(head) set index = search(24,head) IF (index >= 0) Print index Else Print not found in the list EndIF STOP
उदाहरण
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//structure of a node
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node* intoList(int data) {
struct node* newnode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newnode->data = data;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
//funtion to display list
void displayList(struct node *catchead) {
struct node *temp;
if (catchead == NULL) {
printf("List is empty.\n");
return;
}
printf("elements of list are : ");
temp = catchead;
while (temp != NULL) {
printf("%d ", temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
//function to search element
int search(int key,struct node *head) {
int index;
struct node *newnode;
index = 0;
newnode = head;
while (newnode != NULL && newnode->data != key) {
index++;
newnode = newnode->next;
}
return (newnode != NULL) ? index : -1;
}
int main() {
int index;
struct node* head = intoList(9); //inserting elements into a list
head->next = intoList(76);
head->next->next = intoList(13);
head->next->next->next = intoList(24);
head->next->next->next->next = intoList(55);
head->next->next->next->next->next = intoList(109);
displayList(head);
index = search(24,head);
if (index >= 0)
printf("%d found at position %d\n", 24, index);
else
printf("%d not found in the list.\n", 24);
index=search(55,head);
if (index >= 0)
printf("%d found at position %d\n", 55, index);
else
printf("%d not found in the list.\n", 55);
} आउटपुट
यदि हम उपरोक्त प्रोग्राम चलाते हैं तो यह निम्न आउटपुट उत्पन्न करेगा।
elements of list are : 9 76 13 24 55 109 24 found at position 3 55 found at position 4