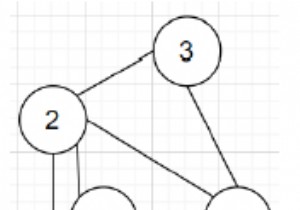
यदि एक निर्देशित ग्राफ दिया गया है, तो निर्धारित करें कि दिए गए ग्राफ में सभी शीर्ष जोड़े (i, j) के लिए एक शीर्ष j दूसरे शीर्ष i से पहुंच योग्य है या नहीं। रीचेबल का मतलब है कि शीर्ष i से j तक का रास्ता है। इस पहुंच-क्षमता मैट्रिक्स को ग्राफ़ का ट्रांजिटिव क्लोजर कहा जाता है। Warshall एल्गोरिथम आमतौर पर किसी दिए गए ग्राफ़ G के ट्रांजिटिव क्लोजर को खोजने के लिए उपयोग किया जाता है। इस एल्गोरिथम को लागू करने के लिए यहां एक C++ प्रोग्राम है।
एल्गोरिदम
Begin 1.Take maximum number of nodes as input. 2.For Label the nodes as a, b, c ….. 3.To check if there any edge present between the nodes make a for loop: for i = 97 to less than 97 + number of nodes for j = 97 to less than 97 + number of nodes if edge is present do, adj[i - 97][j - 97] = 1 else adj[i - 97][j - 97] = 0 end loop end loop. 4.To print the transitive closure of graph: for i = 0 to number of nodes c = 97 + i end loop. for i = 0 to number of nodes c = 97 + i; for j = 0 to n_nodes print adj[I][j] end loop end loop End. के लिए
उदाहरण कोड
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int n_nodes = 20;
int main() {
int n_nodes, k, n;
char i, j, res, c;
int adj[10][10], path[10][10];
cout << "\n\tMaximum number of nodes in the graph :";
cin >>n;
n_nodes = n;
cout << "\nEnter 'y' for 'YES' and 'n' for 'NO' \n";
for (i = 97; i < 97 + n_nodes; i++)
for (j = 97; j < 97 + n_nodes; j++) {
cout << "\n\tIs there an edge from " << i << " to " << j << " ? ";
cin >>res;
if (res == 'y')
adj[i - 97][j - 97] = 1;
else
adj[i - 97][j - 97] = 0;
}
cout << "\nTransitive Closure of the Graph:\n";
cout << "\n\t\t\t ";
for (i = 0; i < n_nodes; i++) {
c = 97 + i;
cout << c << " ";
}
cout << "\n\n";
for (int i = 0; i < n_nodes; i++) {
c = 97 + i;
cout << "\t\t\t" << c << " ";
for (int j = 0; j < n_nodes; j++)
cout << adj[i][j] << " ";
cout << "\n";
}
return 0;
} आउटपुट
Maximum number of nodes in the graph :4 Enter 'y' for 'YES' and 'n' for 'NO' Is there an edge from a to a ? y Is there an edge from a to b ?y Is there an edge from a to c ? n Is there an edge from a to d ? n Is there an edge from b to a ? y Is there an edge from b to b ? n Is there an edge from b to c ? y Is there an edge from b to d ? n Is there an edge from c to a ? y Is there an edge from c to b ? n Is there an edge from c to c ? n Is there an edge from c to d ? n Is there an edge from d to a ? y Is there an edge from d to b ? n Is there an edge from d to c ? y Is there an edge from d to d ? n Transitive Closure of the Graph: a b c d a 1 1 0 0 b 1 0 1 0 c 1 0 0 0 d 1 0 1 0