साइकिल सॉर्ट एक इन-प्लेस, अस्थिर सॉर्टिंग एल्गोरिथम है, एक तुलना सॉर्ट जो सैद्धांतिक रूप से किसी भी अन्य इन-प्लेस सॉर्टिंग एल्गोरिदम के विपरीत, मूल सरणी में लिखने की कुल संख्या के संदर्भ में इष्टतम है। यह इस विचार पर आधारित है कि क्रमबद्ध किए जाने वाले क्रमपरिवर्तन को चक्रों में विभाजित किया जा सकता है, जिसे क्रमबद्ध परिणाम देने के लिए व्यक्तिगत रूप से घुमाया जा सकता है।
लगभग हर दूसरे प्रकार के विपरीत, आइटम को ऐरे में कहीं और नहीं लिखा जाता है, बस उन्हें कार्रवाई के रास्ते से बाहर धकेलने के लिए। प्रत्येक मान या तो शून्य बार लिखा जाता है, यदि यह पहले से ही अपनी सही स्थिति में है या एक बार अपनी सही स्थिति में लिखा गया है। यह एक पूर्ण इन-प्लेस सॉर्ट के लिए आवश्यक ओवरराइट की न्यूनतम संख्या से मेल खाता है।
लिखने की संख्या को कम करना उपयोगी होता है जब कुछ बड़े डेटा सेट पर लिखना बहुत महंगा होता है, जैसे फ्लैश मेमोरी जैसे ईईपीरोम के साथ जहां प्रत्येक लेखन स्मृति के जीवनकाल को कम करता है।
Input: a[]={7,4,3,5,2,1,6}
Output: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 स्पष्टीकरण
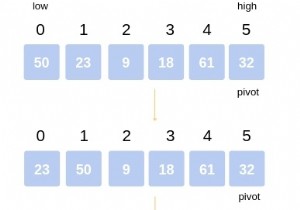
arr[] = {10, 5, 2, 3}
index = 0 1 2 3
cycle_start = 0
item = 10 = arr[0]
Find position where we put the item,
pos = cycle_start
while (arr[i] < item)
pos++;
We put 10 at arr[3] and change item to
old value of arr[3].
arr[] = {10, 5, 2, 10}
item = 3
Again rotate rest cycle that start with index '0'
Find position where we put the item = 3
we swap item with element at arr[1] now
arr[] = {10, 3, 2, 10}
item = 5
Again rotate rest cycle that start with index '0' and item = 5
we swap item with element at arr[2].
arr[] = {10, 3, 5, 10 }
item = 2
Again rotate rest cycle that start with index '0' and item = 2
arr[] = {2, 3, 5, 10}
Above is one iteration for cycle_stat = 0.
Repeat above steps for cycle_start = 1, 2, ..n-2 के लिए उपरोक्त चरणों को दोहराएं उदाहरण
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void cycleSort(int a[], int n) {
int writes = 0;
for (int c_start = 0; c_start <= n - 2; c_start++) {
int item = a[c_start];
int pos = c_start;
for (int i = c_start + 1; i < n; i++)
if (a[i] < item)
pos++;
if (pos == c_start)
continue;
while (item == a[pos])
pos += 1;
if (pos != c_start) {
swap(item, a[pos]);
writes++;
}
while (pos != c_start) {
pos = c_start;
for (int i = c_start + 1; i < n; i++)
if (a[i] < item)
pos += 1;
while (item == a[pos])
pos += 1;
if (item != a[pos]) {
swap(item, a[pos]);
writes++;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
int a[] ={7,4,3,5,2,1,6};
int n = 7;
cycleSort(a, n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << a[i] << " ";
return 0;
}