इस समस्या में हमें एक बाइनरी ट्री दिया जाता है और हमें एक विशेष नोड से dfs करने की आवश्यकता होती है जिसमें हम दिए गए नोड को रूट मान लेते हैं और उससे dfs निष्पादित करते हैं।
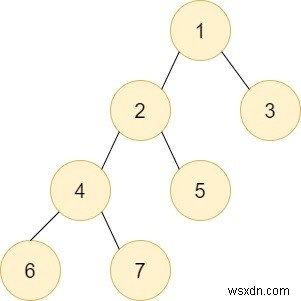
उपरोक्त पेड़ में मान लीजिए कि हमें नोड एफ से डीएफएस करने की आवश्यकता है
इस ट्यूटोरियल में हम कुछ अपरंपरागत तरीकों को लागू करने जा रहे हैं ताकि यह हमारे समय की जटिलता को काफी हद तक कम कर देगा और इस प्रकार हम इस कोड को उच्च बाधाओं के लिए भी चला पाएंगे।
दृष्टिकोण - इस दृष्टिकोण में हम सरल तरीके से नहीं जा रहे हैं, जहां हम हर नोड के लिए केवल dfs लागू करते हैं क्योंकि यह उच्च बाधाओं के लिए काम नहीं करेगा इसलिए हम TLE प्राप्त करने से बचने के लिए कुछ अपरंपरागत तरीकों का उपयोग करने का प्रयास करते हैं।
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 100000
// Adjacency list to store the
// tree nodes connections
vector<int> v[N];
unordered_map<int, int> mape; // will be used for associating the node with it's index
vector<int> a;
void dfs(int nodesunder[], int child, int parent){ // function for dfs and precalculation our nodesunder
a.push_back(child); // storing the dfs of our tree
// nodesunder of child subtree
nodesunder[child] = 1;
for (auto it : v[child]) { // performing normal dfs
if (it != parent) { // as we the child can climb up to
//it's parent so we are trying to avoid that as it will become a cycle
dfs(nodesunder, it, child); // recursive call
nodesunder[child] += nodesunder[it]; // storing incrementing the nodesunder
//by the number of nodes under it's children
}
}
}
// Function to print the DFS of subtree of node
void printDFS(int node, int nodesunder[]){
int ind = mape[node]; // index of our node in the dfs array
cout << "The DFS of subtree " << node << ": ";
// print the DFS of subtree
for (int i = ind; i < ind + nodesunder[node]; i++){ // going through dfs array and then
//printing all the nodes under our given node
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void addEdgetoGraph(int x, int y){ // for maintaining adjacency list
v[x].push_back(y);
v[y].push_back(x);
}
void mark(){ // marking each node with it's index in dfs array
int size = a.size();
// marks the index
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
mape[a[i]] = i;
}
}
int main(){
int n = 7;
// add edges of a tree
addEdgetoGraph(1, 2);
addEdgetoGraph(1, 3);
addEdgetoGraph(2, 4);
addEdgetoGraph(2, 5);
addEdgetoGraph(4, 6);
addEdgetoGraph(4, 7);
// array to store the nodes present under of subtree
// of every node in a tree
int nodesunder[n + 1];
dfs(nodesunder, 1, 0); // generating our nodesunder array
mark(); // marking the indices in map
// Query 1
printDFS(2, nodesunder);
// Query 2
printDFS(4, nodesunder);
return 0;
} आउटपुट
The DFS of subtree 2: 2 4 6 7 5 The DFS of subtree 4: 4 6 7
कोड को समझना
इस दृष्टिकोण में हम dfs के क्रम का पूर्व-गणना कर रहे हैं और इसे एक वेक्टर में संग्रहीत कर रहे हैं, जब हमने dfs का पूर्व-गणना कर लिया है, तो हम प्रत्येक नोड से शुरू होने वाले प्रत्येक उपट्री के तहत मौजूद नोड्स की गणना भी करते हैं और फिर हम सभी के लिए तत्कालीन नोड के शुरुआती इंडेक्स को ट्रैवर्स करते हैं। इसके सबट्री के अंदर मौजूद नोड्स की संख्या।
निष्कर्ष
इस ट्यूटोरियल में, हम एक पेड़ में एक सबट्री के डीएफएस के लिए क्वेरीज़ को हल करने के लिए एक समस्या का समाधान करते हैं। हमने इस समस्या के लिए C++ प्रोग्राम और संपूर्ण दृष्टिकोण (सामान्य) भी सीखा जिसके द्वारा हमने इस समस्या को हल किया।
हम उसी प्रोग्राम को अन्य भाषाओं जैसे C, java, python और अन्य भाषाओं में लिख सकते हैं। आशा है कि आपको यह लेख मददगार लगा होगा।