इस लेख में, हम नीचे दिए गए समस्या कथन के समाधान के बारे में जानेंगे।
समस्या कथन - हमें एक निर्देशित ग्राफ दिया गया है, हमें यह जांचना होगा कि ग्राफ में एक चक्र है या नहीं। आउटपुट सही होना चाहिए यदि दिए गए ग्राफ़ में कम से कम एक चक्र है, अन्यथा गलत है।
आइए अब नीचे दिए गए कार्यान्वयन में समाधान देखें -
उदाहरण
# collections module
from collections import defaultdict
# class for creation of graphs
class Graph():
# constructor
def __init__(self, vertices):
self.graph = defaultdict(list)
self.V = vertices
def addEdge(self, u, v):
self.graph[u].append(v)
def isCyclicUtil(self, v, visited, recStack):
# Marking current node visited and addition to recursion stack
visited[v] = True
recStack[v] = True
# if any neighbour is visited and in recStack then graph is cyclic in nature
for neighbour in self.graph[v]:
if visited[neighbour] == False:
if self.isCyclicUtil(neighbour, visited, recStack) == True:
return True
elif recStack[neighbour] == True:
return True
# pop the node after the end of recursion
recStack[v] = False
return False
# Returns true if graph is cyclic
def isCyclic(self):
visited = [False] * self.V
recStack = [False] * self.V
for node in range(self.V):
if visited[node] == False:
if self.isCyclicUtil(node, visited, recStack) == True:
return True
return False
g = Graph(4)
g.addEdge(0, 3)
g.addEdge(0, 2)
g.addEdge(3, 2)
g.addEdge(2, 0)
g.addEdge(1, 3)
g.addEdge(2, 1)
if g.isCyclic() == 1:
print ("Graph is cyclic in nature")
else:
print ("Graph is non-cyclic in nature") आउटपुट
Graph is cyclic in nature
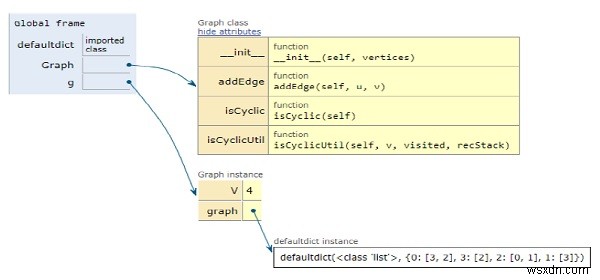
सभी चर स्थानीय दायरे में घोषित किए गए हैं और उनके संदर्भ ऊपर की आकृति में देखे गए हैं।
निष्कर्ष
इस लेख में, हमने सीखा है कि हम एक निर्देशित ग्राफ़ में साइकिल का पता लगाने के लिए एक पायथन प्रोग्राम कैसे बना सकते हैं