एक लूप में एक प्रक्रिया चलाने के मामले पर विचार करें और जब भी कोई बटन क्लिक किया जाता है तो हम लूप को रोकना चाहते हैं। आम तौर पर, प्रोग्रामिंग भाषाओं में, निरंतर जबकि . को रोकने के लिए लूप, हम एक ब्रेक . का उपयोग करते हैं बयान। हालांकि, टिंकर में, जबकि . के स्थान पर लूप, हम उपयोग करते हैं after() परिभाषित फ़ंक्शन को लूप में चलाने के लिए। निरंतर लूप को तोड़ने के लिए, एक वैश्विक बूलियन चर का उपयोग करें जिसे लूप की चल रही स्थिति को बदलने के लिए अद्यतन किया जा सकता है।
दिए गए उदाहरण के लिए,
-
एक वैश्विक चर बनाएं जो ध्वज . के समान कार्य करे एक लूप में।
-
दो बटन परिभाषित करें, प्रारंभ करें और रोकें , निष्पादन शुरू करने और रोकने के लिए।
-
दो कार्यों को परिभाषित करें, on_start() और on_stop() , लूप पर अपडेट देने के लिए।
उदाहरण
# Import the required libraries
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import ttk
# Create an instance of tkinter frame or window
win = Tk()
# Set the size of the window
win.geometry("700x350")
running = True
# Define a function to print the text in a loop
def print_text():
if running:
print("Hello World")
win.after(1000, print_text)
# Define a function to start the loop
def on_start():
global running
running = True
# Define a function to stop the loop
def on_stop():
global running
running = False
canvas = Canvas(win, bg="skyblue3", width=600, height=60)
canvas.create_text(150, 10, text="Click the Start/Stop to execute the Code", font=('', 13))
canvas.pack()
# Add a Button to start/stop the loop
start = ttk.Button(win, text="Start", command=on_start)
start.pack(padx=10)
stop = ttk.Button(win, text="Stop", command=on_stop)
stop.pack(padx=10)
# Run a function to print text in window
win.after(1000, print_text)
win.mainloop() आउटपुट
एक निश्चित स्थिति के लिए लूप का परीक्षण करने के लिए उपरोक्त कोड चलाएँ।
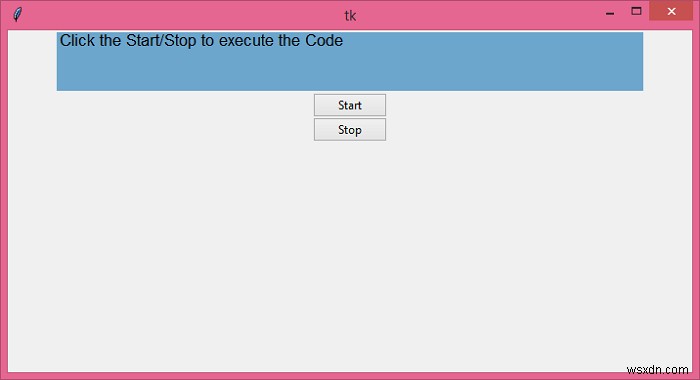
यदि हम उपरोक्त कोड को चलाएंगे और स्टार्ट बटन पर क्लिक करेंगे, तो यह "हैलो वर्ल्ड" टेक्स्ट को एक लूप में प्रिंट करेगा जिसे "स्टॉप" बटन पर क्लिक करके रोका जा सकता है।
Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Process finished with exit code 0