लिनक्स ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम में, एक हटाई गई फ़ाइल ट्रैश में अपना रास्ता खोज लेती है। जब ट्रैश खाली हो जाता है, तो फ़ाइल सिस्टम से हटा दी जाती है। हालाँकि, पुनर्प्राप्ति सॉफ़्टवेयर की बढ़ती मांग के साथ, ट्रैश से हटाई गई फ़ाइलों को एक निश्चित सीमा तक पुनर्प्राप्त किया जा सकता है। इसका अर्थ है कि ट्रैश से निकाली गई फ़ाइल को कभी भी स्थायी रूप से नहीं हटाया गया था, लेकिन वह आपकी आंखों के लिए अदृश्य हो गई थी। फ़ाइल अभी भी आपकी हार्ड ड्राइव पर कहीं अनावश्यक स्थान घेर रही है और केवल तभी पूरी तरह से हटा दी जाएगी जब एक नई फ़ाइल बनाई जाएगी और आपकी हार्ड ड्राइव के उन्हीं क्षेत्रों में संग्रहीत की जाएगी। मूल्यवान डिस्क स्थान को पुनर्प्राप्त करने और फ़ाइल भ्रष्टाचार से बचने के लिए, लिनक्स में फ़ाइल को स्थायी रूप से हटाना महत्वपूर्ण है।
लिनक्स ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम में फ़ाइल को स्थायी रूप से हटाने के लिए यहां कुछ चरण दिए गए हैं।
लिनक्स ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम में मौजूद विविधताओं और कई उपलब्ध डिस्ट्रोस जैसे उबंटू, मिंट, फेडोरा आदि के कारण, लिनक्स में एक फ़ाइल को हटाने के चरण चरणों में भिन्न हो सकते हैं, लेकिन फ़ाइलों और फ़ोल्डरों को हटाने के पीछे मूल अवधारणा समान रहती है। आपकी हार्ड डिस्क को फ़ॉर्मेट किए बिना लिनक्स में निर्देशिकाओं को स्थायी रूप से हटाने वाले सबसे सामान्य चरण हैं:
पद्धति 1. ट्रैश विकल्प हटाएं
एक विकल्प है, जो चयनित होने पर, उपयोगकर्ता को लिनक्स में किसी फ़ाइल को ट्रैश में भेजे बिना सीधे हटाने की अनुमति देता है। इस विकल्प को सक्षम करना विभिन्न प्रकार के लिनक्स में भिन्न होता है, लेकिन इस सुविधा के पीछे उपयोग की जाने वाली प्रक्रिया नीचे उल्लिखित दो में से कोई भी हो सकती है:
- ट्रैश लिमिट कम करें।
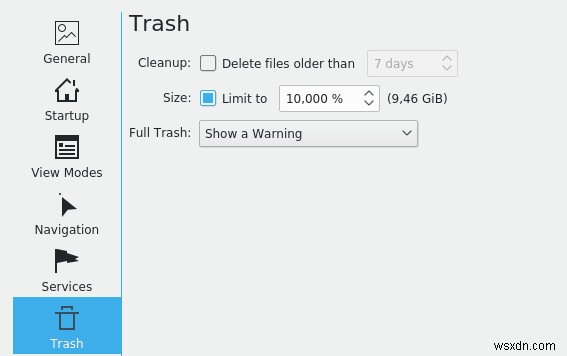
यदि आपका लिनक्स डिस्ट्रो डॉल्फिन फ़ाइल प्रबंधक का समर्थन करता है, तो वरीयताओं तक पहुंचें और आकार लेबल वाले बॉक्स के बगल में एक चेकमार्क लगाएं और प्रतिशत सीमा को न्यूनतम मूल्य पर सेट करें। यह सुनिश्चित करेगा कि निर्धारित आकार से बड़ी सभी फ़ाइलें ट्रैश में संग्रहीत नहीं की जाएंगी और स्थायी रूप से हटा दी जाएंगी।
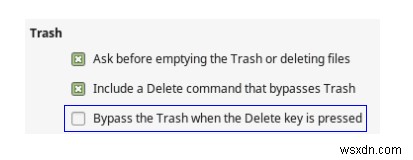
- यदि आपका लिनक्स नॉटिलस या निमो फ़ाइल प्रबंधक का उपयोग कर रहा है, तो आपको फ़ाइल प्रबंधक वरीयताएँ में एक विकल्प मिलेगा जिससे डिलीट कुंजी दबाए जाने पर बायपास ट्रैश को सक्षम किया जा सके। यह किसी भी हटाई गई फ़ाइल को ट्रैश में नहीं ले जाएगा।
विधि 2. आप फ़ाइलों को कभी भी श्रेड कर सकते हैं
जीएनयू प्रोजेक्ट द्वारा विकसित, श्रेड लिनक्स ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम में एम्बेडेड एक प्रोग्राम है, जिसका उपयोग लिनक्स में फ़ाइल को स्थायी रूप से हटाने के लिए किया जा सकता है। श्रेड का उपयोग करके परीक्षण के नाम से दस्तावेज़ फ़ाइल को हटाने वाली कमांड लाइन है:
shred -uvz -n 2 Test.doc
"यू" पैरामीटर फ़ाइल को ओवरराइट करने से पहले हटा देता है।
"वी" पैरामीटर वर्बोज़ जानकारी प्रदर्शित करता है।
"Z" पैरामीटर हटाए गए डेटा की पुनर्प्राप्ति की किसी भी संभावना को रोकता है।
"-n 2" पैरामीटर अतिरिक्त सुरक्षा के लिए अतिरिक्त पास निर्दिष्ट करता है।
In case, there are multiple files in a folder by the name of Music and you want to delete all of them, then use this command:
shred -uvz -n 2 Music/*.*
The name of the folder is specified as Music and the Asterix with a period and followed by another Asterix specifies to delete a file in Linux irrespective of their name or extension.
Method 3. Use Wipe.
The Linux Software distribution centre will allow you to install Wipe on your Linux Distro. It is like Shred program and is easy to use. The command line for deleting a file through Wipe is:
wipe Music/song1.mp3
Wipe is more secure than Shred and this means it is time-consuming as well. It also requests a confirmation from the user. To quicken the process, use appropriate flags such as:
f:using this flag will remove the confirmation.
c:wipe the file despite permissions.
q:quicken the process by bypassing all the security passes.
r:delete from a folder in Linux.
The simple Wipe command with all the flags would now appear as:
wipe -rfcq Music/song1.mp3
Method 4. Use Secure Delete.
Another tool that ensures removal of data from a hard drive is SRM, which is bundled in the Secure Delete suite. It is a quite efficient and quick tool and can even delete a directory in Linux. The command to delete a file is:
SRM is one of the tools in the Secure Delete suite of tools that specializes in secure removal of data from your HDD. It’s held by many as the best tool for this job.
Srm Music/song1.mp3
Like Wipe, deleting a file by SRM is a time-consuming process and can be made aster using flags. Some important flags are:
z:your file will be deleted and overwritten by zeros replacing the file for extra security.
v:this flag will provide verbose information about the process.
r:this will enable the recursive mode for subfolders.
1:the number one. This will reduce the time taken to complete the process.
The new command would then be:
srm -rlvz Music/Song1.jpg
Method 5. Install Bleachbit (GUI)
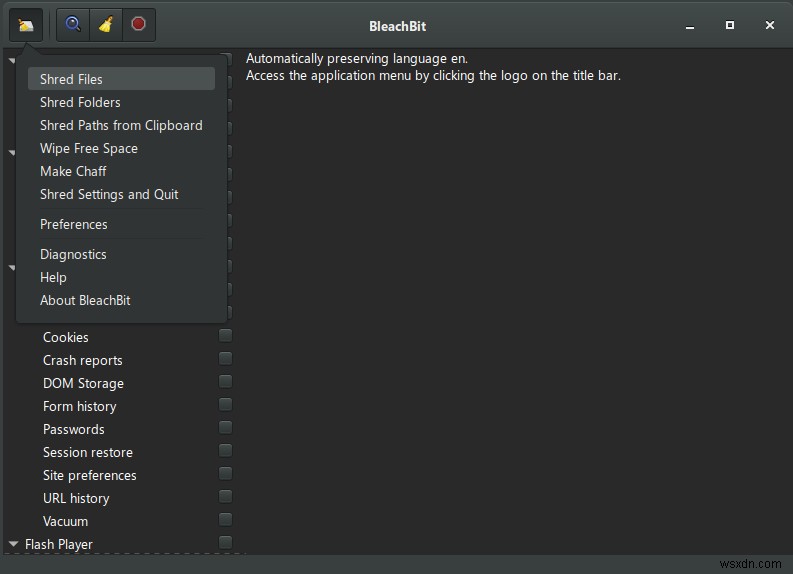
One of the best tools to find and delete unwanted files and even delete folders in Linux operating system is Bleachbit. It is known to free up space by securely erasing data that has not been used for a long time and can be used manually to target a few files that need to be deleted. It can be installed through the software centre by using the following command:
sudo apt install bleachbit
Once installed, run the interface and click on EDIT and choose Preferences. In the General Tab, there would be a list of different options. Place a checkmark in the box beside the option labelled as “Overwrite contents of files to prevent recovery”.
Next, to permanently delete a file on Linux, click File and choose Shred option. A prompt box will appear confirming your action. Click on Delete, and that will the last of the files selected.
The Final Word On Delete A File In Linux.
Although using a Linux operating system is a different experience, it is not difficult. All you must know the functions and features that are embedded in Linux. Being an Open-source, Linux has many options to do the same task, and these are some of the easy ones to delete a file in Linux permanently. Do subscribe to Systweak Blogs and our YouTube Channel for more tech-related updates.